UK Driving Theory Test Practice Questions and Answers
UK Driving Theory Test Practice Questions and Answers
Note: There are 1000+ questions in the DVSA theory test question bank, and your 57 minute theory exam will contain 50 multiple choice questions, of which you must score 43 correct to pass. The following revision guide is a close resemblance of the style of questions and answers you can expect and they will help you to pass as they will give you an idea of what to expect. The answers to the UK theory test can all be found in: -
1. The main cause of skidding is:
A. the vehicle
B. the driver
C. the road
D. the weather
2. You may remove your seat belt temporarily when carrying out a manoeuvre that involves:
A. Reversing
B. An emergency stop
C. A hill start
D. Driving slowly
3. Your car hits a pedestrian at 60 kph. The pedestrian will:
A. Certainly be killed
B. Probably be killed
C. Certainly survive
D. Probably survive
4. You are in very heavy downpour. Your overall stopping distance is likely to be:
A. Doubled
B. No different
C. Up to ten times greater
D. Halved
5. What is the national speed limit for cars in the left-hand lane of a three-lane motorway?
A. 60 mph
B. 50 mph
C. 70 mph
D. 80 mph
6. You are turning left into a side road. What hazards should you be especially aware of?
A. One-way street
B. Parked vehicles
C. Pedestrians
D. Traffic congestion
7. The fluid level in your battery is low. What should you top it up with?
A. Battery acid
B. Distilled water
C. Engine coolant
D. Engine oil
8. You are driving along a wet road. How can you tell if your vehicle is aquaplaning?
A. The engine noise will increase
B. The engine will stall
C. The steering will feel very heavy
D. The steering will feel very light
9. When you approach a bus that is about to move off from a bus stop you should:
A. Get past before it moves
B. Signal left and wave the bus on
C. Allow it to pull away, if it is safe to do so
D. Flash your headlights as you approach

10. The national speed limit for cars and motorcycles on a single carriageway road is
A. 40 mph
B. 30 mph
C. 60 mph
D. 50 mph
11. You are dazzled by oncoming headlights when driving at night. What should you do?
A. Drive faster past the oncoming car
B. Flash your lights
C. Brake hard
D. Slow down or stop
12. You should not use a mobile phone whilst driving
A. Because it might distract your attention from the road ahead
B. Unless you are able to drive one handed
C. Because reception is poor when the engine is running
D. Until you are satisfied that no other traffic is near
13. What does this sign mean?

A. Roundabout
B. No entry
C. No stopping
D. Crossroads
14. You have stopped at a pedestrian (zebra) crossing to allow pedestrians to cross. You should:
A. Wait until they have crossed
B. Wait, revving your engine
C. Edge your vehicle forward slowly
D. Signal to pedestrians to cross
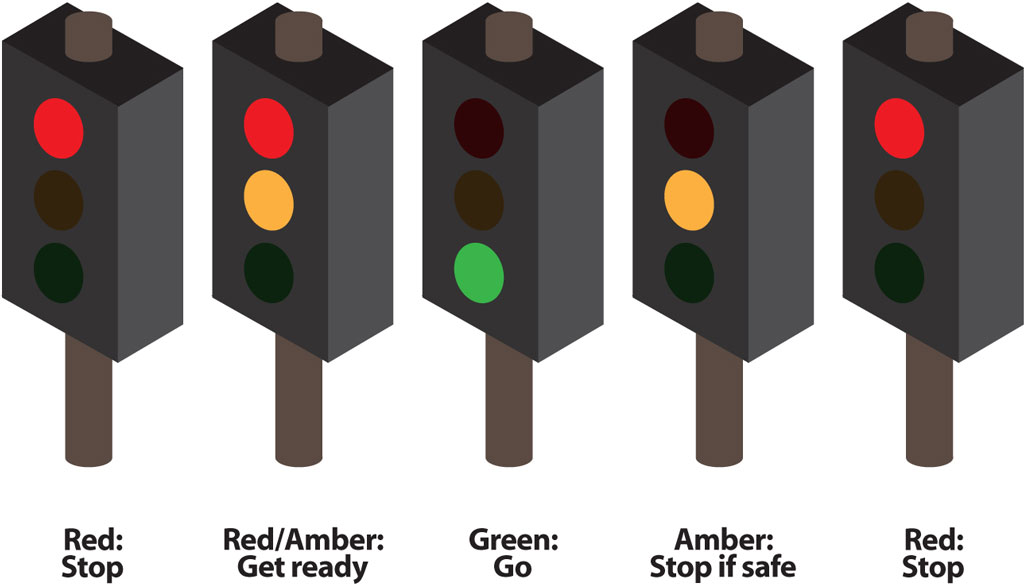
15. A red traffic light means:
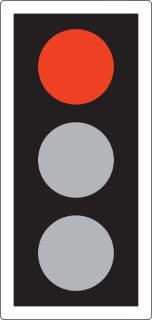
A. You must stop behind the white stop line
B. You may drive straight on if there is no other traffic
C. You must slow down and prepare to stop
D. You may turn left if it is safe to do so
16. When emerging from a side road into a queue of traffic which cars can be especially difficult to see?
A. Motorcycles
B. Milk floats
C. Tractors
D. Cars
17. What is the meaning of this sign?
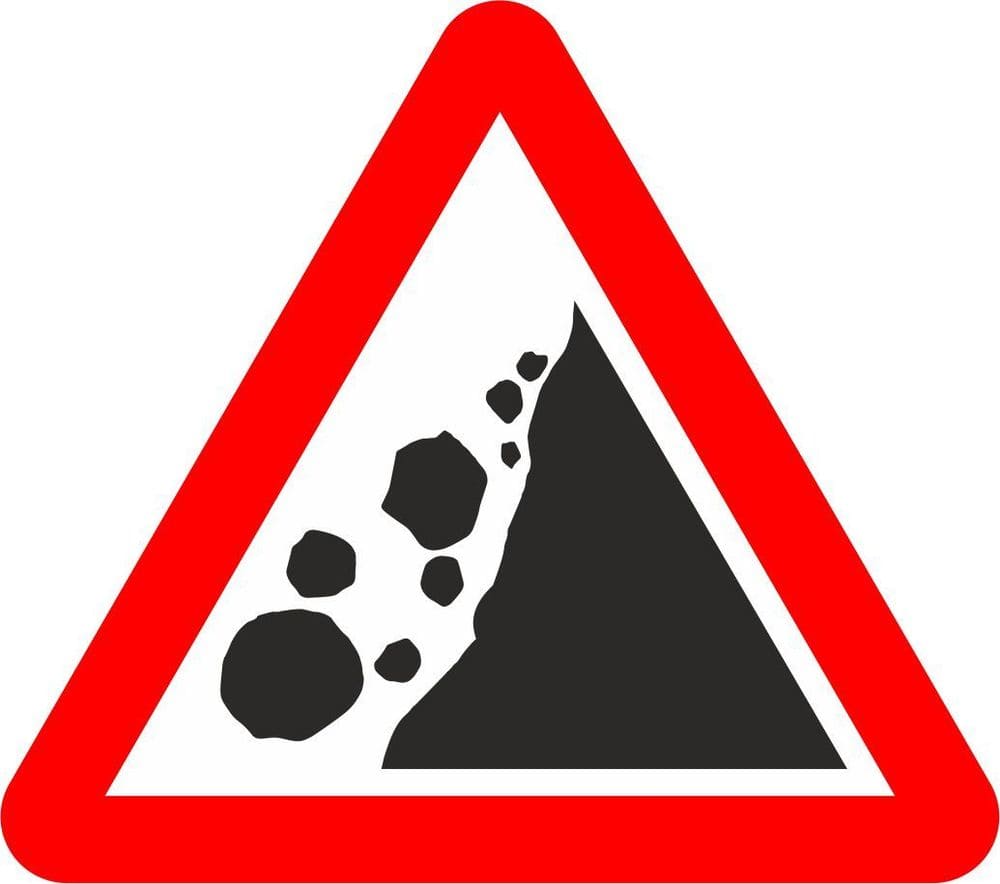

A. Side winds Quayside or river bank
B. Falling or fallen rocks
C. Cliff face ahead
18. What should you use the horn for?
A. To alert others to your presence
B. To greet other road users
C. To allow you right of way
D. To signal you annoyance
19. Why should you always reduce your speed when driving in fog?
A. Because it is more difficult to see events ahead
B. Because the engine`s colder
C. Because you could be dazzled by other people`s fog lights
D. Because the brakes do not work as well
20. A casualty is not breathing normally. At what rate should chest compressions should be given?
A. 50 per minute
B. 100 per minute
C. 200 per minute
D. 250 per minute
21. As a driver, how can you help the environment?
A. By driving faster
B. By using leaded fuel
C. By driving with your windows down
D. By reducing your speed
22. Whilst driving, the fog clears and you can see more clearly. You must remember to
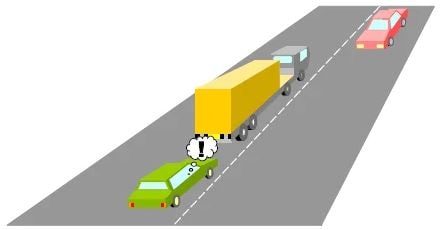
A. Switch off the demister
B. Reduce your speed
C. Switch off the fog lights
D. Close any open windows
23. Overloading your vehicle can seriously affect?
A. The Handling
B. The steering
C. Your comfort
D. Your ability to change gears
24. Some two-way roads are divided into three lanes. Why are these particularly dangerous?
A. Traffic uses the middle lane for emergencies only
B. Traffic can travel faster in poor weather conditions
C. Traffic can overtake on the left
D. Traffic in both directions can use the middle lane to overtake
25. You are approaching this roundabout and see the cyclist signal right. Why is the cyclist keeping to the left?
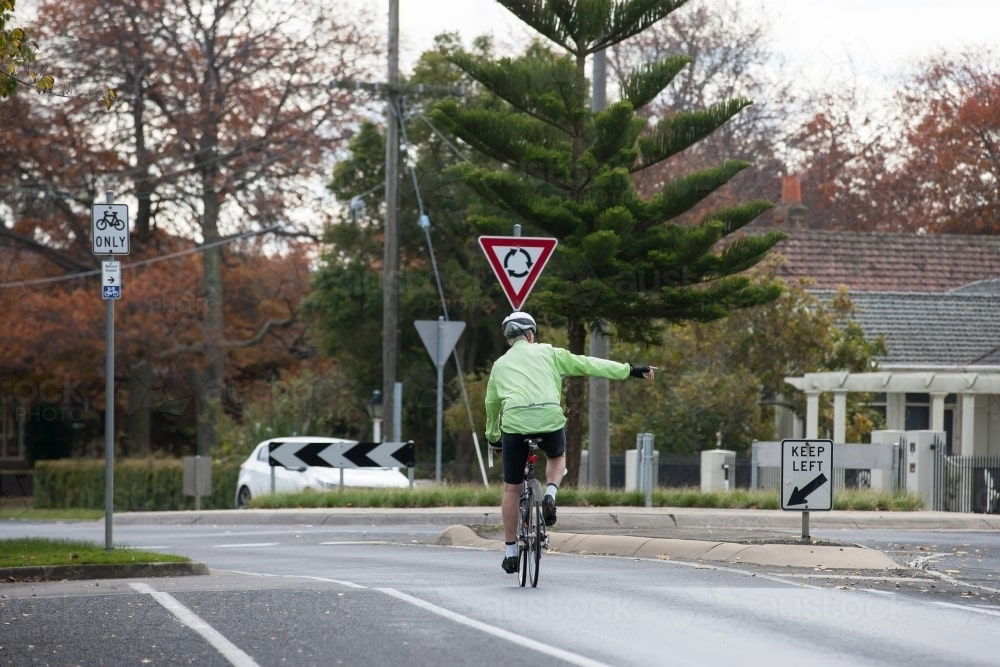

A. It is quicker route for cyclist
B. The cyclist is going to turn left instead
C. The cyclist is slower and more vulnerable
D. The cyclist thinks The highway Code does not apply to bicycles
26. 'Red Routes' in major cities have been introduced to
A. Raise the speed limits
B. Help the traffic flow
C. Provide better parking
D. Allow lorries to load more freely
27. Motorcyclists are more at risk to be injured from other road users because they
A. Are more likely to break down than other motorists
B. Are more difficult to see than other drivers
C. Are less experienced that other drivers
D. Are always faster than other drivers
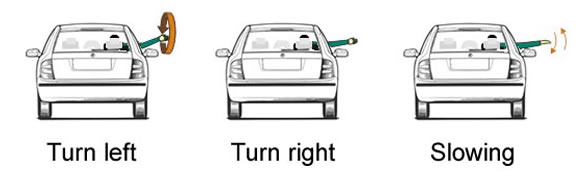
28. The driver of this car is giving an arm signal. What is he about to do?

A. Go straight ahead
B. Turn to the left
C. Let pedestrians cross
D. Turn to the right
29. Someone is waiting to cross at a zebra crossing. They are standing on the pavement. You should normally:
A. Stop, let them cross, wait patiently
B. Go on quickly before they step onto the crossing
C. Ignore them as they are still on the pavement
D. Stop before you reach the zigzag lines and let them cross
30. 'Tailgating' usually means
A. Using the rear door of a hatchback car
B. Driving with rear fog lights on
C. Reversing into a parking space
D. Following another vehicle too closely
31. When being followed by an ambulance showing a flashing blue light you should:
A. Accelerate fast to get away from it
B. Maintain your speed and course
C. Brake harshly and immediately stop in the road
D. Pull over as soon as safely possible to let it pass
32. A heavy load on your roof rack will:
A. Reduce the stopping distance
B. Make the steering lighter
C. Reduce stability
D. Improve the road holding
33. What does this traffic sign mean?
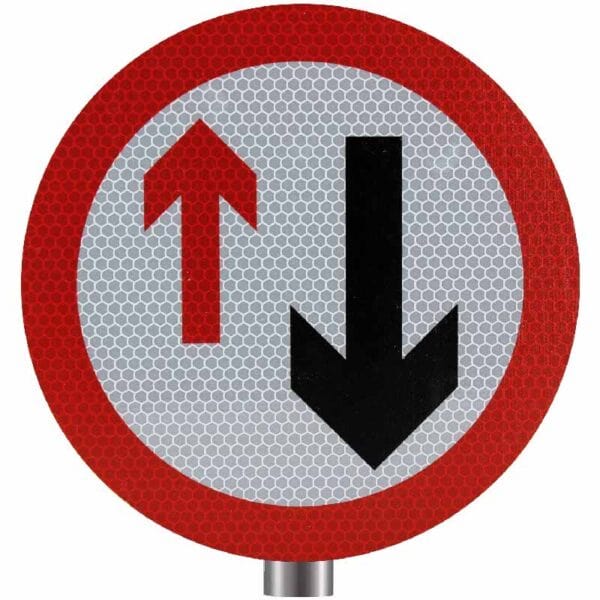

A. Two way traffic
B. No overtaking allowed
C. One-way traffic only
D. Give priority to oncoming traffic
34. Which of the following types of glasses should NOT be worn when driving at night?
A. Round
B. Tinted
C. Half-moon
D. Bi-focal
35. Super trams or Light Rapid Transit (LRT) systems are environmentally friendly because
A. They use diesel power
B. They use electric power
C. They use quieter roads
D. They do not operate during rush hour
36. What lights and why must you put them on when going through a tunnel?
A. Dipped-beam and front and/or rear Fog lights to see and be seen clearly.
B. Main-beam to see clearly where you are going.
C. No lights are necessary as tunnels have their own lighting.
D. Hazard warning lights so nobody drives too near.
E. Dipped-beam to help you see and also be clearly seen by others.
37. You start to feel tired whilst driving, you should?
A. Turn on the radio and listen to loud music
B. Stop at a safe place and rest
C. Decrease your speed
D. Increase your speed to reduce your journey time
38. You are driving past a lane of parked cars and you notice a ball bouncing out into the road ahead. What should you do?
A. Stop and wave the children across to fetch their ball
B. Continue driving at the same speed and sound your horn
C. Slow down and be prepared to stop for children
D. Continue driving at the same speed and flash your headlights
39. In daylight, an approaching motorcyclist is using a dipped headlight. Why?
A. To stop the battery overcharging
B. So that the rider can be seen more easily
C. The rider is inviting you to proceed
D. To improve the rider’s vision
40. Who is responsible for ensuring that a vehicle is fully road worthy when driven on a public road?
A. Nobody in particular
B. Your mechanic
C. You, the driver
D. The VRT tester
41. Using front/rear fog lights in good visibility will:
A. Improve your visibility
B. Dazzle other drivers
C. Increase your awareness
D. Flatten the battery
42. A strong cross wind is least likely to affect which of these vehicles?
A. Motorcycles
B. High-sided vehicles
C. Cars
D. Cyclists
43. Where may you overtake on a one-way Street?
A. Only on the left-hand side
B. Only on the right-hand side
C. Overtaking is not allowed
D. Either on the right or the left
44. You are approaching a zebra crossing. Pedestrians are waiting to cross. You should:
A. Slow down and prepare to stop
B. Wave at them to cross the road
C. Give way to elderly and infirm only
D. Use your headlights to indicate they can cross
45. You are carrying a child in your car. They are under three years of age. Which of these is a suitable restraint?
A. An adult seat belt
B. A child seat
C. An adult lap belt
D. An adult holding a child
46. If you are feeling tired it is best to stop as soon as you can. Until then you should:
A. Ensure a supply of fresh air
B. Increase your speed to find a stopping place quickly
C. Keep changing speed to improve concentration
D. Gently tap the steering wheel
47. You think the driver in the vehicle in front has forgotten to cancel their right indicator. You should
A. Overtake on the left if there is room
B. Flash your lights to alert the driver
C. Sound your horn before overtaking
D. Stay behind and not overtake
48. When following a large vehicle you should stay well back because
A. It allows the driver to see you in the mirror
B. It helps the large vehicle to stop more easily
C. It allows you to corner more quickly
D. It helps you to keep out of the wind
49. Following a collision someone has suffered a burn. The burn needs to be cooled. What is the shortest time it should be cooled for?
A. 15 minutes
B. 5 minutes
C. 10 minutes
D. 20 minutes
50. A pedestrian with a white stick and red band is
A. Deaf and dumb
B. Blind only
C. Deaf and blind
D. Over 65 years old
51. There is a tractor ahead of you. You wish to overtake but you are NOT sure if it is safe to do so. You should:
A. Follow another overtaking vehicle through
B. Not overtake if you are in doubt
C. Sound your horn to the slow vehicle to pull over
D. Speed through but flash your lights to oncoming traffic
52. You are driving behind three cyclists. They approach a roundabout in the lefthand lane. In which direction should you expect the cyclists to go?
A. Left
B. Right
C. Straight ahead
D. Any direction
53. When overtaking which routine should you use?
A. Mirrors, position, speed, look, mirrors, signal, manoeuvre
B. Look, mirrors, position, mirrors, signal, manoeuvre
C. Speed, mirrors, look, signal, manoeuvre
D. Mirrors, speed, position, look, mirrors, signal, manoeuvre
54. How can you help to prevent your car radio from being stolen?
A. Hide the radio with a blanket
B. Install a security-coded radio
C. Park near a busy junction
D. Park in an unlit area
55. What is the meaning of this sign?
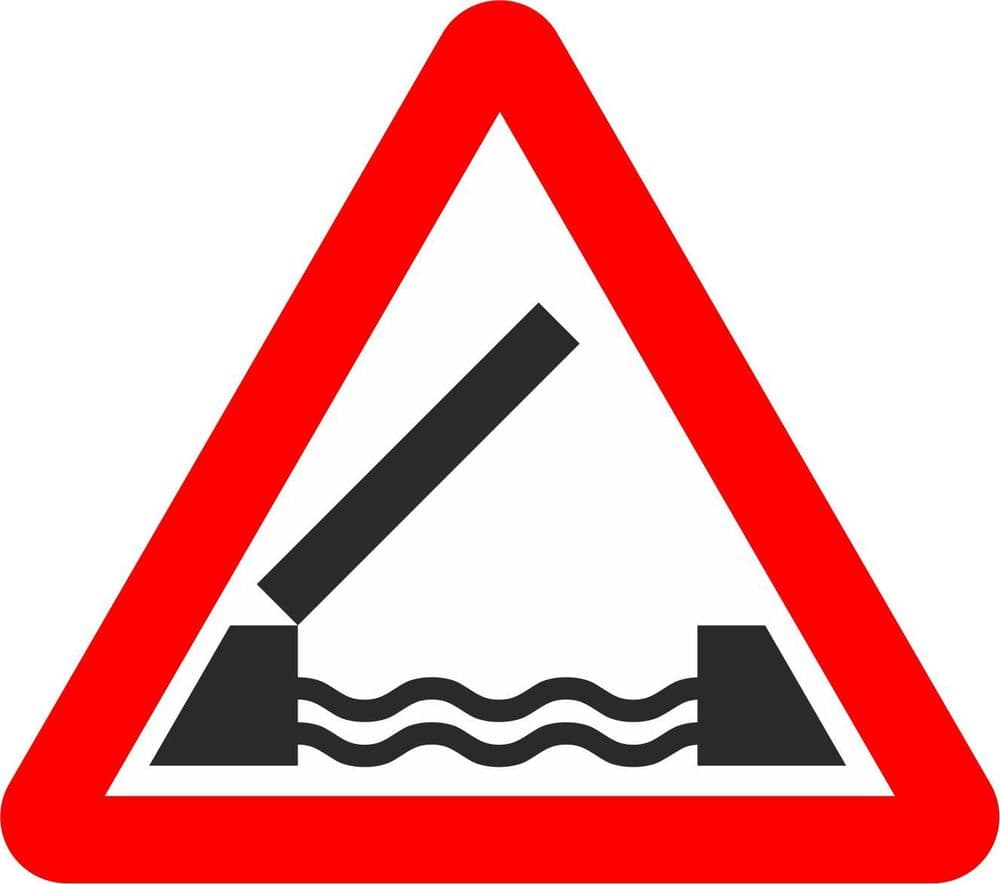

A. Toll bridge ahead
B. Opening or swing bridge ahead
C. Road ahead closed
D. Humpback bridge ahead
56. Your overall stopping distance will be much longer when:
A. Driving on a very hot day
B. Driving in strong winds
C. Driving in fog
D. Driving in rain
57. You are on a long, downhill slope. What should you do to help control the speed of your car?
A. Grip the handbrake firmly
B. Apply the parking brake gently
C. Select a lower gear
D. Select neutral
58. Why could keeping the clutch down or selecting neutral for long periods of time be dangerous?
A. Engine damage may be caused
B. Fuel spillage will occur
C. You will have less steering and braking control
D. It will wear tyres out more quickly
59. You have been convicted of driving whilst unfit through drink or drugs. You will find this is likely to cause the cost of one of the following to rise considerably. Which one?
A. Insurance premiums
B. Vehicle test certificate
C. Road fund licence
D. Driving licence
60. Anti-lock brakes prevent wheels from locking. This means the tyres are less likely to
A. Skid
B. Aquaplane
C. Wear
D. Puncture
61. Any load that is carried on a roof rack MUST be:
A. As light as possible
B. Carried only when strictly necessary
C. Covered with plastic sheeting
D. Securely fastened when driving
62. What is the maximum number of penalty points that will automatically disqualify a driver who holds a provisional driving licence?
A. 10 points during any one year period
B. 18 points over a two year period
C. 15 points over a five 5 year period
D. 4 points a year over a 3 year period
E. 12 points at any time during a 3 year period
63. You can use the engine of your vehicle as a brake by
A. By selecting fifth gear
B. By selecting a lower gear
C. By travelling with the clutch pressed down
D. By turning the engine off
64. When should you use front and rear fog lights?
A. When it is raining and just in case the roads are slippery.
B. When going through tunnels.
C. When the road is unlit by street lamps or they are not working.
D. During any time of the day or night to make sure that other road users see me.
E. When visibility is considerably reduced because of fog.
65. What does this sign mean?
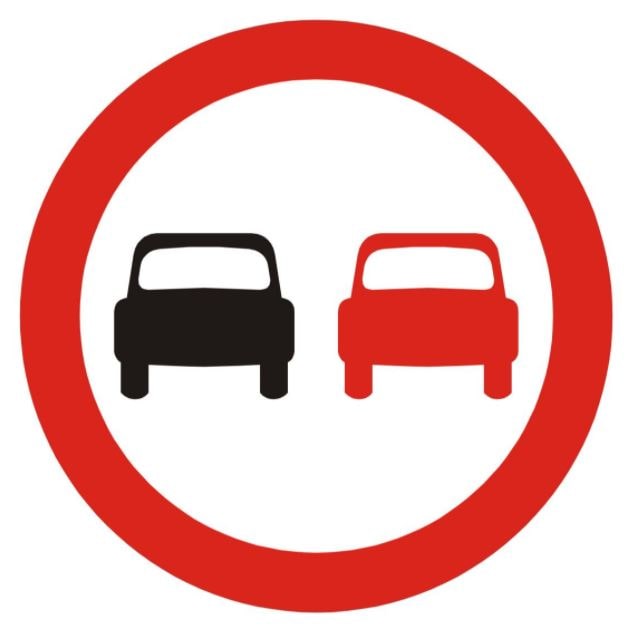

A. No motor vehicles
B. You have priority
C. No overtaking
D. Two-way traffic
66. A driver has had a few alcoholic drinks, what advice should you give them?
A. Take extra care when driving home
B. Drink several cups of coffee before driving home
C. Take a short sleep before driving home
D. Do not drive home
67. You may only enter a box junction when:

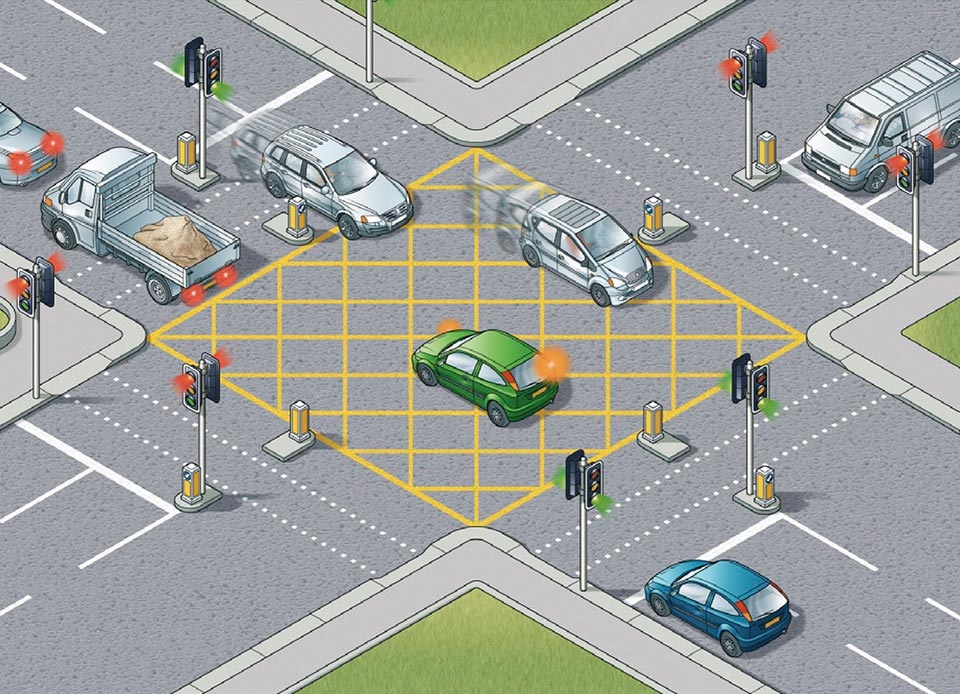
A. Your exit road is clear
B. You need to turn left
C. There are less than two vehicles in front of you
D. The traffic lights show green
68. What does this sign mean?
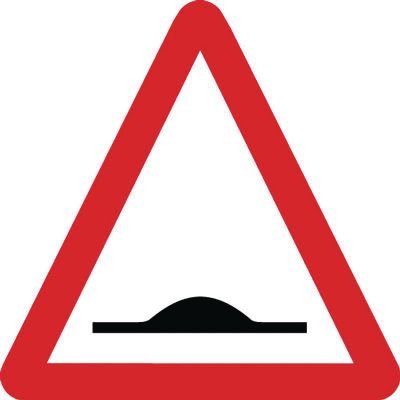

A. Humps in the road
B. Humpback bridge
C. Entrance to tunnel
D. Soft verges
69. You go to a social event and need to drive a short time afterwards. What precaution should you take?
A. Avoid drinking alcohol on an empty stomach
B. Avoid drinking alcohol completely
C. Drink plenty of milk before drinking alcohol
D. Drink plenty of coffee after drinking alcohol
70. Apart from suffering any punishment according to law, what will a disqualified driver has to do to obtain a driving licence?
A. Simply re-sit and pass the test of skills and behaviour.
B. Re-apply as for a new driver after expiry of disqualification period and must re-sit and pass both the theory test and test of skills and behaviour.
C. Pay any outstanding fines, submit a new licence application and re-sit and pass the theory test at any time during disqualification period.
D. Wait for any disqualification period to pass and apply for a duplicate driving licence.
71. You are on a narrow road at night. A slower-moving vehicle ahead has been signaling right for some time. What should you do?
A. Overtake on the left
B. Signal right and sound your horn
C. Wait for the signal to be cancelled before overtaking
D. Flash your headlights before overtaking
72. You want to turn right from a main road into a side road. Just before you turn you should
A. Cancel your right-turn signal
B. Stop and set the handbrake
C. Check for traffic overtaking on your right
D. Select first gear
73. The main purpose of a box junction is
A. To prevent junctions becoming blocked by queuing traffic
B. To speed traffic up
C. To stop you turning right at a crossroads
D. To slow traffic down
74. As you approach a pelican crossing the lights change to green but elderly people are halfway across. You should:
A. Wait because they will take longer to cross
B. Rev your engine to make them hurry
C. Flash your lights in case they have not heard you
D. Wave them to cross as quickly as they can
75. You are approaching a right-hand bend. You should:
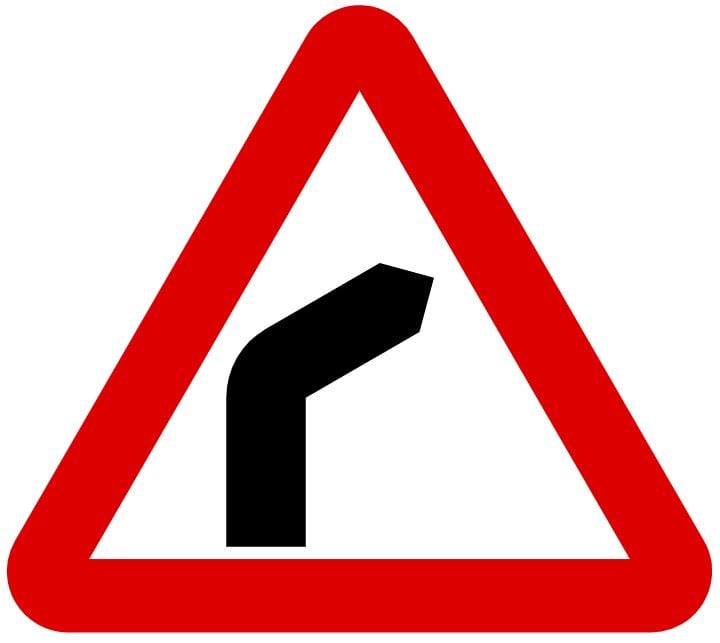

A. Keep well to the left for a better view around the bend
B. Keep well to the left as it makes the bend faster
C. Keep well to the right to avoid anything in the gutter
D. Keep well to the right to make the bend less sharp
76. When are passengers allowed to ride in a caravan that is being towed?
A. When travelling on minor roads
B. When they are over 18 years old
C. When travelling on motorways
D. Never
77. Your car is fitted with power assisted steering. This will make the steering seem
A. Noisier
B. Lighter
C. Heavier
D. Quieter
Power assisted steering is a system for reducing the steering effort on cars by using an external power source to assist in turning the wheels
78. You are dazzled at night by the lights of the vehicle behind you. You should:
A. Set your mirror to anti-dazzle
B. Brake sharply to a stop
C. Set your mirror to dazzle the other driver
D. Switch your rear lights on and off
79. A fundamental rule when driving on a dual carriageway is:
A. Use the lane that has least traffic
B. Keep to the left lane unless overtaking
C. Try to keep above 50 kph to prevent congestion
D. Overtake on the side that is clearest
80. You are driving on an icy road. How can you avoid wheel spin?
A. Drive at a slow speed in as high gear as possible
B. Use the handbrake if the wheels start to slip
C. Brake gently and repeatedly
D. Drive in a low gear at all times
81. This marking appears on the road just before a
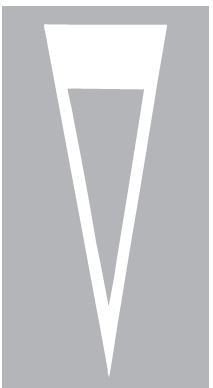
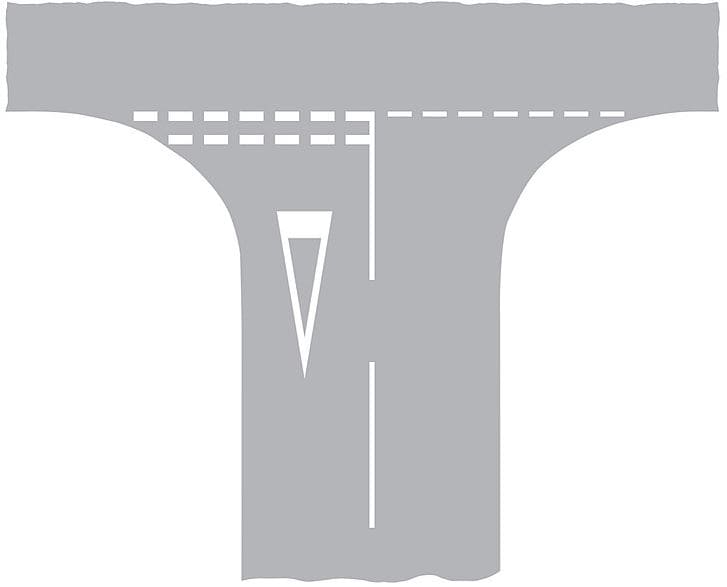
A. No entry sign
B. No through road sign
C. Give way sign
D. Stop sign
82. What does tailgating mean?
A. When a vehicle is with its back doors open
B. When stationary vehicles are too close in a queue
C. When a vehicle delivering goods has its tailgate down
D. When a driver is following another vehicle too closely
83. You are driving a slow moving car on a narrow winding road. In order to let other vehicles overtake you should
A. Wave to them to pass
B. Pull in safely when you can
C. Keep left and hold your speed
D. Show a left turn signal
84. On the dual carriageway the hard shoulder should be used
A. For a short rest when tired
B. To answer a mobile phone
C. When an emergency arises
D. To check a road atlas
85. What does this sign mean?

A. Crossroads
B. Level crossing without gate
C. Ahead only
D. Level crossing with gate
86. While driving a vehicle, at what distance MUST you be able to read a number plate?
A. 30 meters (98 feet)
B. 20.5 meters (67 feet)
C. 10 meters (33 feet)
D. 15 meters (49 feet)
87. A learner driver you are following stalls at a junction. What should you do?
A. Sound your horn and flash your lights
B. Steer around them and drive on
C. Shout instructions
D. Be patient and wait for them to move on
88. An MOT certificate is normally valid for
A. Three years after the date it was issued
B. 30,000 miles
C. 10,000 miles
D. One year after the date it was issued
89. A cycle lane is marked by a solid white line. You must not drive or park in it
A. At any time
B. During its period of operation
C. During the rush hour
D. If a cyclist is using it
90. At which pedestrian crossing are cyclists allowed to ride across?
A. Puffin
B. Toucan
C. Zebra
D. Pelican
There are five (5) different types of pedestrian crossings; Puffin, Zebra, Toucan, Pelican and Pegasus


91. A police officer orders you to stop and he finds you have a faulty tyre. Who is responsible for the tyre?
A. Whoever issued the VRT certificate
B. The previous owner
C. Whoever services the car
D. You, the driver
92. You are driving in traffic at the speed limit for the road. The driver behind is going to overtake. You should:
A. Keep a steady course and allow the driver behind to overtake
B. Accelerate to get away from the driver behind
C. Move closer to the car ahead, so the driver behind has no room to overtake
D. Wave the driver behind to overtake when it is safe
93. You are driving past a lane of parked cars and you notice a ball bouncing out into the road ahead. What should you do?
A. Stop and wave the children across to fetch their ball
B. Slow down and be prepared to stop for children
C. Continue driving at the same speed and sound your horn
D. Continue driving at the same speed and flash your headlights
94. You are towing a caravan. Which is the safest type of rear-view mirror to use?
A. Interior wide-angle mirror
B. Ordinary interior mirror
C. Ordinary door mirrors
D. Extended-arm side mirrors
95. You are trying to move off on snow. You should use
A. The lowest gear you can
B. The highest gear you can
C. A high engine speed
D. The handbrake and footbrake together
96. When going straight ahead at a roundabout you should:
A. Indicate right when approaching the roundabout
B. Indicate left when approaching the roundabout
C. Not indicate at any time
D. Indicate left before leaving the roundabout
97. You are driving in fog. Why should you keep well back from the vehicle in front?

A. In case it stops suddenly
B. In case its brake lights dazzle you
C. In case its fog lights dazzle you
D. In case it changes direction suddenly
98. What does this sign mean?

A. No through road
B. Telephone box ahead
C. T-junction
D. Toilet ahead
99. Apart from suffering any punishment according to law, what will a disqualified driver has to do to obtain a driving licence?
A. Re-apply as for a new driver after expiry of disqualification period and must re-sit and pass both the theory test and test of skills and behaviour.
B. Pay any outstanding fines, submit a new licence application and re-sit and pass the theory test at any time during disqualification period.
C. Simply re-sit and pass the test of skills and behaviour.
D. Wait for any disqualification period to pass and apply for a duplicate driving licence.
100. You are taking drugs that are likely to affect you driving. What should you do?
A. Drive only for short distances
B. Only drive if accompanied by a full licence holder
C. Limit your driving to essential journeys
D. Seek medical advice before driving
101. Motorcycles ride in day light with their headlights switched on because
A. It is legal requirement
B. There is a speed trap ahead
C. They need to be seen
D. There are speed humps ahead
102. In daylight, an approaching motorcyclist is using a dipped headlight. Why?
A. To stop the battery overcharging
B. The rider is inviting you to proceed
C. To improve the rider’s vision
D. So that the rider can be seen more easily
103. You want to turn right from a main road into a side road. Just before you turn you should
A. Select first gear
B. Stop and set the handbrake
C. Cancel your right-turn signal
D. Check for traffic overtaking on your right
104. Which of the following are at greatest risk from other road users?
A. Lorry drivers
B. Busy bus drivers
C. Motorcycles
D. Learner car drivers
105. When MUST you use dipped lights during the day?
A. When parking
B. Along narrow streets
C. All the time
D. In poor visibility
106. Before reversing you should always check:
A. Your side mirrors
B. Your rear view mirror
C. The area behind you
D. All round
107. What do these road markings mean?

A. No stopping or parking permitted.
B. Central limit of dual carriageway and may be crossed only when overtaking.
C. Lines on the road just to mark the lanes and guide traffic flows, which have no legal or safety implications.
D. Continuous solid double white line (Centre line) which vehicles must not drive over, across or astride except to enter a side road, unless prohibited from doing so by appropriate signage.
108. When about to overtake a long vehicle or lorry you should:
A. Drive close to the lorry in order to pass more quickly
B. Sound the horn to warn the driver that you are there
C. Stay well back from the lorry to obtain a better view
D. Flash your lights and wait for the driver to signal when it is safe
109. You are travelling along the left-hand lane of a three-lane motorway. Traffic is joining from a slip road. You should
A. Move to another lane
B. Race the other vehicles
C. Switch on your hazard lights
D. Maintain a steady speed
110. Another driver does something that upsets you. You should:
A. Let them know how you feel
B. Sound your horn
C. Try not to react
D. Flash your headlights several times
111. You are driving and ahead of you there is a vehicle with a flashing amber beacon. This means it is:
A. Slow moving
B. A school crossing patrol
C. A doctor’s car
D. Broken down
112. What does the term 'blind spot' mean for a driver?
A. An area not covered by your mirrors
B. An area not covered by your headlights
C. An area covered by your right-hand mirror
D. An area covered by your left-hand mirror
113. You enter a road where there are road humps. You should:

A. Always keep to the maximum legal speed
B. Accelerate quickly between each one
C. Drive slowly at school times only
D. Maintain a reduced speed throughout
114. You see a pedestrian with a white stick and red band. This means that the person is
A. Physically disabled
B. Deaf and blind
C. Deaf only
D. Blind only
115. When should you give signals?
A. In traffic only during the hours of darkness or in bad weather.
B. To give you priority over other traffic when changing lanes or before pulling out.
C. Only when joining a dual carriageway from a slip road so you don't have to give way
D. At all times in order to alert other road users of your intended actions.
116. As you approach a pelican crossing the lights change to green but elderly people are halfway across. You should:
A. Rev your engine to make them hurry
B. Wave them to cross as quickly as they can
C. Wait because they will take longer to cross
D. Flash your lights in case they have not heard you
117. At traffic lights, amber on its own means:

A. Go if the way is clear
B. Go if no pedestrians are crossing
C. Prepare to go
D. Stop at the stop line
the-highway-code-light-signals-controlling-traffic.pdf
118. You meet an obstruction on your side of the road. You should:
A. Give way to oncoming traffic
B. Wave oncoming vehicles through
C. Drive on; it is your right of way
D. Accelerate to get past first
119. You will use more fuel if your tyres are
A. Of different makes
B. New and hardly used
C. Under-inflated
D. Over-inflated
120. To correct a rear-wheel skid you should
A. Apply your handbrake
B. Steer away from it
C. Not steer at all
D. Steer into it
121. What does this sign mean?

A. No vehicles over 30 tonnes
B. End of 30 kph zone
C. New speed limit 20 kph
D. Minimum speed limit 30kph
122. You stopped for pedestrians waiting to cross at a zebra crossing. They did not start to cross. What should you do?
A. Wave them to cross
B. Be patient and wait
C. Sound your horn
D. Drive on
123. A driver has had a few alcoholic drinks, what advice should you give them?
A. Drink several cups of coffee before driving home
B. Take extra care when driving home
C. Take a short sleep before driving home
D. Do not drive home
124. You are driving in town. There is a bus at the bus stop on the other side of the road. Why should you be careful?
A. Pedestrians may come from behind the bus
B. The bus may have broken down
C. The bus may remain stationary
D. The bus may move off suddenly
125. You are travelling at the legal speed limit. A vehicle comes up quickly behind, flashing its headlights. You should
A. Accelerate to make a gap behind you
B. Maintain your speed to prevent the vehicle from overtaking
C. Touch the brakes sharply to show your brake lights
D. Allow the vehicle to overtake
126. When you apply to renew your vehicle Excise Duty (tax disc) you must have
A. A valid driving licence
B. The old tax disc
C. Valid insurance
D. The handbook
127. A toucan crossing is different from other crossings because
A. A traffic warden controls it
B. Two flashing lights control it
C. Moped riders can use it
D. Cyclists can use it
128. The vehicle you are driving pulls to one side when you brake. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
A. Low levels of power steering fluid
B. Poorly adjusted brakes
C. A faulty handbrake
D. Incorrect tyre pressure
129. You are driving in very wet weather. Your vehicle begins to slide. This affect is called:
A. Weaving
B. Fading
C. Hosing
D. Aquaplaning
130. You are driving at night on an dark, unlit road following a slower moving vehicle. You should:
A. Use dipped beam headlights
B. Use full beam headlights
C. Switch off you headlights
D. Flash your headlights
131. Driving with under-inflated (low) tyres can affect
A. Engine temperatures
B. Oil pressure
C. Fuel consumption
D. Judgment of the driver
132. The aim of an Active Traffic Management scheme on a motorway is to
A. Prevent overtaking
B. Reduce congestion
C. Prevent tailgating
D. Reduce rest stops
133. What should a driver do at a pelican crossing when the red and amber lights are on?
A. Always wait for the green light before proceeding
B. Give way to any pedestrians on the crossing
C. Wait for the red-and amber light before proceeding
D. Signal the pedestrian to cross
134. An elderly person’s driving ability could be affected because they may be unable to:
A. Understand road signs
B. React very quickly
C. Obtain car insurance
D. Give signals correctly
135. Motorcars must first have an MOT certificate when they are
A. Seven (7) years old
B. One (1) year old
C. Five (5) years old
D. Three (3) years old
136. While driving a vehicle, at what distance MUST you be able to read a number plate?
A. 30 meters (98 feet)
B. 15 meters (49 feet)
C. 10 meters (33 feet)
D. 20.5 meters (67 feet)
137. You MUST obey signs giving orders. These signs are mostly in:
A. Red triangles
B. Green rectangles
C. Blue rectangles
D. Red circles
138. You are parking your car. You have some valuables, which you are unable to take with you. What should you do?
A. Lock then out of sight
B. Park in an unlit side road
C. Put them under the driver's seat
D. Park near a police station
139. 'Red Routes' in major cities have been introduced to
A. Help the traffic flow
B. Allow lorries to load more freely
C. Provide better parking
D. Raise the speed limits
140. In freezing conditions you should expect stopping distances to increase by up to
A. Four (4) times
B. Ten (10) times
C. Five (5) times
D. Seven (7) times
141. You should avoid 'coasting' your car because it could:
A. Damage the suspension
B. Flatten the battery
C. Increase tyre wear
D. Reduce steering control
142. Front fog lights may be used ONLY if:
A. They are fitted above the bumper
B. An audible warning device is used
C. They are not as bright as the headlights
D. Visibility is seriously reduced
143. It is essential that tyre pressures be checked regularly. When should this be done?
A. When the tyres are hot
B. After filling the vehicle with fuel
C. After a long journey
D. When the tyres are cold
144. You are approaching a small roundabout. The long vehicle in front is signaling left but is positioned over to the right. You should:
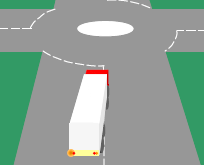
A. Sound your horn
B. Keep well back
C. Overtake on the left
D. Follow the same course as the lorry
145. You take some cough medicine given to you by a friend. What should you do before driving?
A. Check the label to see if the medicine will affect your driving
B. Drink some strong coffee one hour before driving
C. Ask your friend if taking the medicine affected their driving
D. Drive a short distance to see if the medicine is affecting your driving
146. You are approaching two cyclists. They approach a roundabout in the left-hand lane. In which direction should you expect the cyclists to go?
A. Any direction
B. Right
C. Left
D. Straight ahead
147. Front fog lights may be used ONLY if :
A. You wish to overtake in bad weather
B. Visibility is seriously reduced
C. They prevent headlights glare on a wet road
D. Fitted by manufacturer
148. As a driver, how can you help the environment?
A. By reducing your speed
B. By using leaded fuel
C. By driving faster
D. By driving with your windows down
149. Excessive or uneven wear in one or more tyres can be caused by faults in the:
A. Steering Wheel
B. Exhaust system
C. Gearbox
D. Braking system
150. You will help your environment if you:
A. Drive continually using full choke
B. Walk or cycle when you can
C. Accelerate and brake sharply
D. Reduce the tyre pressure
151. When driving through a tunnel you should
A. Look out for variable message signs
B. Always use your windscreen wipers
C. Use your air conditioning system
D. Switch on your rear fog lights
152. You may drive over a footpath:
A. If no pedestrians are near
B. To gain lawful access into a property
C. When the pavement is very wide
D. To overtake slow-moving traffic
153. What is the meaning of this traffic sign?

A. Bus lane ahead
B. End of two-way road
C. Give priority to vehicles coming towards you
D. You have priority over vehicles coming towards you
154. You must not reverse:
A. In a built-up area
B. Into a side road
C. For longer than necessary
D. For more than a car’s length
155. You are approaching traffic lights. Red and amber are showing. This means:

A. Pass the lights if the road is clear
B. There is a fault with the lights – take care
C. The lights are about are about to change to red
D. Wait for the green light before you pass the lights
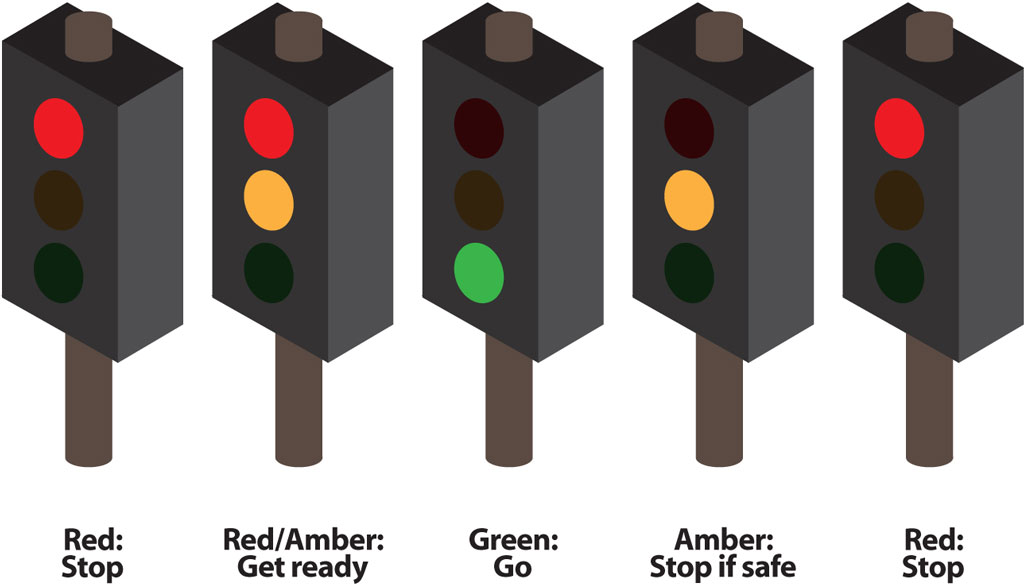
156. Braking hard at a high speed on a sharp bend can make your vehicle
A. More stable
B. Stall
C. Corner safely
D. Unstable
157. You must NOT sound your horn
A. Between 10 pm and 6 am in a built-up area
B. Between 11.30 pm and 7 am in a built-up area
C. Between 11.30 pm and 6 am on any road
D. At any time in a built-up area
158. You are following a large lorry on a wet road. Spray makes it difficult to see. You should:

A. Drop back until you can see better
B. Speed up and overtake quickly
C. Put your headlights on full beam
D. Keep close to the lorry, away from the spray
159. What does the sign mean?
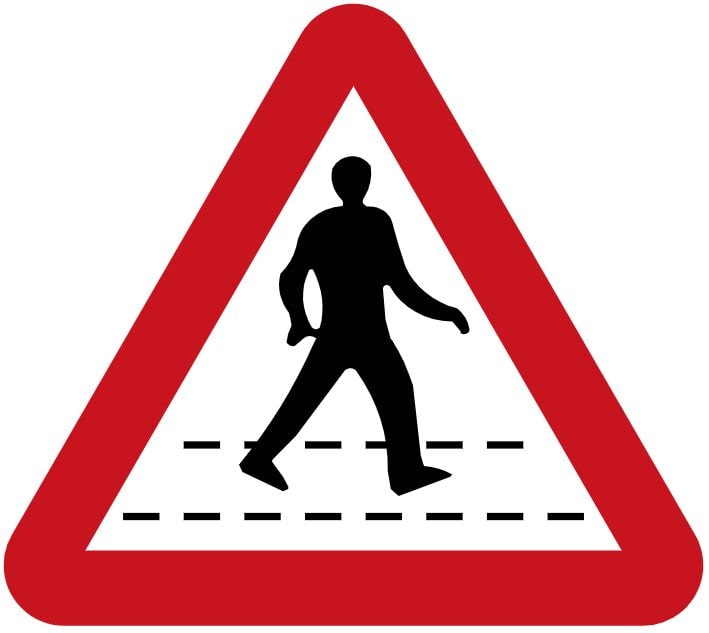

A. No pedestrians allowed
B. Pedestrian crossing ahead
C. School crossing patrol
D. Pedestrian zone – no vehicles
160. There has been a collision. A motorcyclist is lying injured and unconscious. Unless it's essentially why should you usually NOT attempt to remove their helmet?
A. This could result in more serious injury
B. Because you could scratch the helmet
C. They will get too cold if you do this
D. Because they may not want you to
161. A driver does something that upsets you. You should
A. Let them know how you feel
B. Try not to react
C. Flash your headlights several times
D. Sound your horn
162. Your overall stopping distance will be longer when driving:
A. In fog
B. At night
C. In strong winds
D. In the rain
163. You are driving past parked cars. You notice a bicycle wheel sticking out between them. What should you do?
A. Slow down and be prepared to stop for a cyclist
B. Brake sharply and flash your headlights
C. Slow down and wave the cyclist across
D. Accelerate past quickly and sound your horn
164. Which of the following cars will use blue flashing beacons?
A. Doctor on call
B. Motorway maintenance
C. Police patrol
D. Breakdown recovery
165. What does this sign mean?
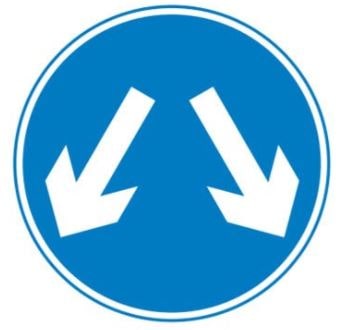
A. Approaching traffic passes you on both sides
B. Pass either side to get to the same destination
C. Turn off at the next available junction
D. Give way to oncoming vehicles
The Highway Code - Traffic Signs Signs with blue circles but no red border mostly give positive instruction. Blue circles will usually give compulsory instructions such as: vehicles may pass either side to reach the same destination, mini-roundabout (give way to traffic from the immediate right) or proceed in the direction indicated by the arrow:
166. As a driver what do you understand by the term 'Blind Spot'?
A. An area covered by your right hand mirror
B. An area not seen in your mirrors
C. An area covered by your left hand mirror
D. An area not covered by your headlights
167. After a breakdown you need to rejoin the main carriageway of a multilane- carriageway from the hard shoulder. You should:
A. Move out onto the carriageway then build up your speed
B. Wait on the hard shoulder until someone flashes their headlights at you
C. Gain speed on the harder shoulder before moving out onto the carriageway
D. Move out onto the carriageway using your hazard lights
168. Why should you always reduce your speed when driving in fog?
A. Because it is more difficult to see events ahead
B. Because the brakes do not work as well
C. Because the engine`s colder
D. Because you could be dazzled by other people`s fog lights
169. You lose your way on a busy road. What is the best action to take?
A. Check a map, and keep going with the traffic flow
B. Shout to other drivers to ask them the way
C. Stop at traffic lights and ask pedestrians
D. Turn into a side road, stop and check a map
170. To supervise a learner driver you must:
A. Be at least 23
B. Be an approved driving instructor
C. Hold an advanced driving certificate
D. Have held a full licence for at least 5 years
171. Why should you be parked before using a mobile phone?
A. Because reception is better when stopped
B. Because the car electrics will be affected
C. So control of your vehicle is not affected
D. So a proper conversation can be held
172. You are about to go down a steep hill. To control the speed of your car you should:
A. Select a low gear and use the brakes carefully
B. Select a high gear and use the brakes carefully
C. Select a low gear and avoid using the brakes
D. Select a high gear and use the brakes firmly
173. You should ONLY flash your headlights to other road users
A. To show that you are giving way
B. To show that you are about to reverse
C. To let them know that you are there
D. To tell the that you have right of way
174. You arrive at the scene of a motorcycle accident. No other vehicle is involved. The rider is unconscious, lying in the middle of the road. The first thing you should do is:
A. Move the rider out of the road
B. Warn other traffic
C. Clear the road of debris
D. Give the rider reassurance
175. An MOT certificate is normally valid for
A. 30,000 miles
B. One year after the date it was issued
C. 10,000 miles
D. Three years after the date it was issued
176. In what situation are other drivers allowed to flash their headlights at you?
A. To warn you danger is ahead
B. To tell you that they are giving way to you
C. To warn you of their presence
D. To warn you when you're breaking the speed limit
177. New petrol-engined cars have to be fitted with catalytic converters. The reason for this is to
A. Reduce harmful exhaust emissions
B. Allow the exhaust system to be recycled
C. Control exhaust noise levels
D. Prolong the life of the exhaust system
178. When should you switch on your hazard warning lights?
A. When you are towing a broken down vehicle
B. When you cannot avoid causing an obstruction
C. When you are parked on double yellow lines
D. When you are driving slowly due to bad weather
179. You are following other vehicles in fog with your lights on. How else can you reduce the chances of being involved in an accident?
A. Keep close to the vehicle in front
B. Keep together with the faster vehicles
C. Reduce your speed and increase the gap
D. Use your main beam instead of dipped headlights
180. You are in a line of traffic. The driver behind you is following very closely. What action should you take?
A. Slow down, gradually increasing the gap between you and the vehicle in front
B. Ignore the following driver and continue to travel within the speed limit
C. Signal left and wave the following driver past
D. Move over to a position just left of the centre line of the road
181. Before driving anyone else’s motor vehicle you should make sure that:
A. Your own vehicle has insurance cover
B. The vehicle is insured for your use
C. The vehicle owner has third party insurance cover
D. The owner has left the insurance documents in the vehicle
182. You are approaching a small roundabout. The long vehicle in front is signaling left but is positioned over to the right. You should:
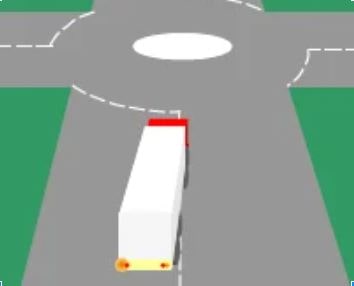
A. Keep well back
B. Sound your horn
C. Overtake on the left
D. Follow the same course as the lorry
183. When going straight ahead at a roundabout you should:
A. Indicate right when approaching the roundabout
B. Indicate left before leaving the roundabout
C. Indicate left when approaching the roundabout
D. Not indicate at any time
184. Your indicators may be difficult to see in bright sunlight. What should you do?
A. Touch the brake several times to show the stop lamp(s)
B. Give an arm signal as well as using your indicator
C. Turn as quickly as you can
185. You must NOT sound your horn
A. Between 11.30 pm and 7 am in a built-up area
B. Between 10 pm and 6 am in a built-up area
C. At any time in a built-up area
D. Between 11.30 pm and 6 am on any road
186. You must not reverse
A. For more than a car's length
B. In built-up areas
C. For longer than necessary
D. Into a side road
187. Why are place names printed on the road surface?
A. To enable you to change lanes early
B. To prevent you changing lanes
C. To warn you of oncoming traffic
D. To restrict the flow of traffic
188. Whilst driving on the motorway you have to slow down quickly due to a hazard. What should you do?
A. Sound your horn
B. Switch on the headlights to full beam
C. Switch on your fog light
D. Switch on your hazard lights
189. Which of the following statements relates to Tailgating
A. Park too close to the tail lift platform of a truck.
B. Driving so close and in such a way that you bully and intimidate the vehicle in front to force it to speed up or get out of your way
C. Driving too close to the vehicle in front creating a hazardous situation in that if it had to stop suddenly, you will be unable to avoid a collision.
D. Swerving from lane to lane and getting as close to the vehicle in front so you get to your destination faster.
190. After driving out of fog and when visibility has returned to normal, you must
A. Use your headlights on dipped beam
B. Switch off your fog lights
C. Use your windscreen wipers
D. Keep your rear fog light on
191. You are driving towards a pedestrian(zebra) crossing. Waiting to cross is a person in a wheelchair. You should:
A. Wave to the person to wait
B. Wave to the person to cross
C. Be prepared to stop
D. Continue on your way
192. Why could keeping the clutch down or selecting neutral for long periods of time be dangerous?
A. You will have less steering and braking control
B. Fuel spillage will occur
C. Engine damage may be caused
D. It will wear tyres out more quickly
193. A driver has had a few alcoholic drinks, what advice should you give them?
A. Take a short sleep before driving home
B. Drink several cups of coffee before driving home
C. Take extra care when driving home
D. Do not drive home
194. What does this sign mean?
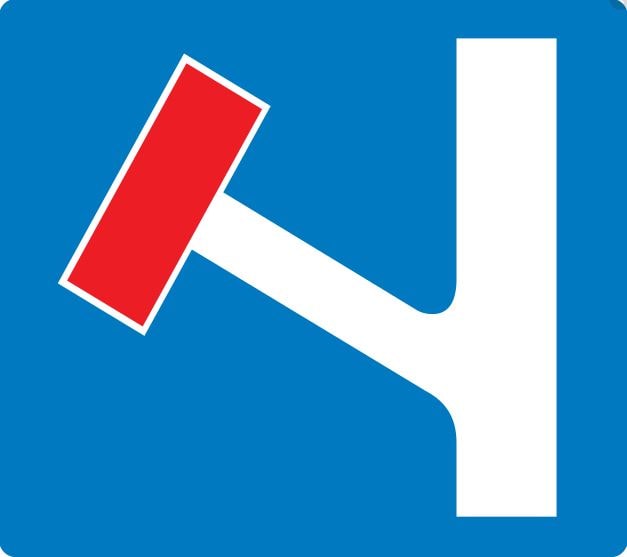

A. Turn left for ferry terminal
B. No through road on the left
C. No entry for traffic turning left
D. Turn left for parking area
195. Your car is fitted with power assisted steering. This will make the steering seem
A. Heavier
B. Noisier
C. Quieter
D. Lighter
196. Catalytic converters are fitted to make the
A. Engines produce more power
B. Exhaust fumes cleaner
C. Engines run quietly
D. Exhaust systems easier to replace
197. 'Tailgating' usually means
A. Driving with rear fog lights on
B. Following another vehicle too closely
C. Reversing into a parking space
D. Using the rear door of a hatchback car
198. Which of these vehicles is LEAST likely to be affected by strong crosswinds?
A. Motorcyclists
B. High-sided vehicles
C. Cars
D. Cyclists
199. A toucan crossing is different from other crossings because
A. Cyclists can use it
B. A traffic warden controls it
C. Two flashing lights control it
D. Moped riders can use it
200. What is the national speed limit, unless otherwise indicated, on dual carriageways for cars and motorcycles?
A. 50 mph
B. 70 mph
C. 80 mph
D. 100 mph
201. The main cause of brake pedal fade is:
A. The brakes out of adjustment
B. The brakes overheating
C. Oil in the brakes
D. Air in brake fluid
202. A strong cross wind is least likely to affect which of these vehicles?
A. High-sided vehicles
B. Motorcycles
C. Cyclists
D. Cars
203. You are following a vehicle on a wet and slippery road. You should leave a time gap of at least
A. Two (2) seconds
B. Three (3) seconds
C. Four (4) seconds
D. One (1) second
204. If you see a pedestrian carrying a white stick, this shows that the person is: This shows that the person is:
A. Elderly
B. Deaf
C. Disabled
D. Blind
205. When driving through a tunnel you should
A. Look out for variable message signs
B. Use your air conditioning system
C. Always use your windscreen wipers
D. Switch on your rear fog lights
206. When driving through a Ford or flood water, what gear should you use?
A. Reverse
B. First or second
C. Fifth
D. Third
E. Fourth
207. What is the national speed limit for cars and motorcycles when travelling in the right-hand lane of a motorway?
A. 70 mph
B. 50 mph
C. 80 mph
D. 60 mph
208. If you are at a junction with limited visibility, you should:
A. Creep forward, looking to the left
B. Be ready to move off quickly
C. Creep forward, looking to the right
D. Creep forward, looking both ways
209. You are driving past parked cars. You notice a wheel of a bicycle sticking out between them. What should you do?
A. Slow down and be prepared to stop for a cyclist
B. Accelerate past quickly and sound your horn
C. Slow down and wave the cyclist across
D. Brake sharply and flash your headlights
210. Whilst driving, the fog clears and you can see more clearly. You must remember to
A. Switch off the demister
B. Close any open windows
C. Switch off the fog lights
D. Reduce your speed
211. Super trams or Light Rapid Transit (LRT) systems are environmentally friendly because
A. They use diesel power
B. They use electric power
C. They do not operate during rush hour
D. They use quieter roads
212. When should you give signals?
A. To give you priority over other traffic when changing lanes or before pulling out.
B. In traffic only during the hours of darkness or in bad weather.
C. At all times in order to alert other road users of your intended actions.
D. Only when joining a dual carriageway from a slip road so you don't have to give way
It is important to let other road users to know your intension.
213. What shape is a STOP sign?
A. Octagonal
B. Square
C. Circular
D. Triangular
214. You are invited to a pub lunch. You know that you will have to drive in the evening. What is your best course of action?
A. Eat a hot meal with your alcohol drinks
B. Have some milk before drinking alcohol
C. Avoid mixing your alcoholic drinks
D. Not drink any alcohol at all
215. You are driving at night on an dark, unlit road following a slower moving vehicle. You should:
A. Flash your headlights
B. Use dipped beam headlights
C. Use full beam headlights
D. Switch off you headlights
216. When a roof rack is not in use it should be removed. Why?
A. It is illegal
B. It will waste fuel
C. It will affect your braking
D. It will affect the suspension
217. At a puffin crossing, which colour follows the green signal?
A. Flashing green
B. Flashing amber
C. Steady red
D. Steady amber
218. You are driving a slow moving car on a narrow winding road. You should
A. Pull in safely when you can, to let following vehicles overtake
B. Wave following vehicles past you if you think they can overtake quickly
C. Keep well out to stop vehicles overtaking dangerously
D. Give a left signal when it is safe for vehicles to overtake you
219. Who has priority at an unmarked crossroads?

A. The driver who is going faster
B. The driver on the wider road
C. No one
D. The driver of the larger vehicle
220. You are driving downhill. There is a car parked on the other side of the road partly blocking the road. Large, slow lorries are coming towards you. You should:
A. Pull over on the right behind the parked car
B. Speed up and get past quickly
C. Slow down and give way
D. Keep going because you have the right of way
221. You MUST obey signs giving orders. These signs are mostly in
A. Red circles
B. Blue rectangles
C. Red Triangles
D. Green rectangles
222. You keep well back while waiting to overtake a large lorry. Another car fills the gap. You should:
A. Flash your headlights
B. Sound your horn
C. Start to overtake
D. Drop back further
223. What does this sign mean?

A. No footpath ahead
B. Pedestrian crossing ahead
C. School crossing ahead
D. Pedestrians only ahead
224. What is the meaning of this sign?

A. Trams only
B. Level crossing without barrier or gate
C. Level crossing with barrier or gate
D. Trams crossing ahead
225. Where should you take particular care to look out for motorcyclists and cyclists?
A. At junctions
B. On one-way streets
C. At zebra crossings
D. On dual carriageways
226. Whilst driving you have an accident in which someone is injured. You must report this to the police within
A. 7 days
B. 36 hours
C. 12 hours
D. 24 hours
227. When you approach a bus that is about to move off from a bus stop you should:

A. Allow it to pull away, if it is safe to do so
B. Get past before it moves
C. Flash your headlights as you approach
D. Signal left and wave the bus on
228. If you are feeling tired it is best to stop as soon as you can. Until then you should:
A. Gently tap the steering wheel
B. Increase your speed to find a stopping place quickly
C. Keep changing speed to improve concentration
D. Ensure a supply of fresh air
https://ukdrivingtheory.com/question_list.php
229. You are on a dual carriageway. Ahead you see a vehicle with an amber flashing light. What could this be?
A. An ambulance
B. A fire engine
C. A disabled person`s vehicle
D. A doctor on call
230. Where are you most likely to be affected by a side wind?
A. On a narrow country lane
B. On an open stretch of road
C. On a long, straight road
D. On a busy stretch of road
231. When travelling in very heavy rain your overall stopping distance is likely to be
A. Quadrupled
B. Doubled
C. The same as normal
D. Trebled
232. A VRT certificate is normally valid for:
A. Two (2) years after the date it was issued
B. 10,000 miles
C. One year after the date it was issued
D. 30,000 miles
233. A horse rider is in the left-hand lane approaching a roundabout. The driver behind should expect the rider to:
A. Go in any direction
B. Go ahead
C. Turn left
D. Turn right
234. When should you use front and rear fog lights?
A. When visibility is considerably reduced because of fog.
B. When the road is unlit by street lamps or they are not working.
C. When it is raining and just in case the roads are slippery.
D. During any time of the day or night to make sure that other road users see me.
E. When going through tunnels.
235. What does this sign mean?

A. Ring road
B. Mini-roundabout
C. No vehicles
D. Roundabout
236. You are coming up to a roundabout and a cyclist is signaling to turn right. What should you do
A. Give the cyclist plenty of room
B. Give a horn warning
C. Signal the cyclist to move across
D. Overtake on the right
237. What is the meaning of this sign?

A. Traffic queues likely
B. Pedestrian crossing ahead
C. Light signals ahead at a level crossing
D. Accident black spot ahead
238. To drive on the road learners MUST
A. Have taken professional instruction
B. Have no penalty points on their licence
C. Apply for a driving test within 12 months
D. Have a signed, valid provisional licence
239. What do these zigzag lines at pedestrian crossings mean?

A. No parking at any time
B. Parking allowed only for a short time
C. Sounding horns is not allowed
D. Slow down to 20kph
240. What is the meaning of this sign?

A. Holiday route ahead
B. Low bridge ahead
C. Tunnel ahead
D. Tourist route ahead
241. What does tailgating mean?
A. Following another vehicle too closely
B. Driving with rear fog lights on
C. Reversing into a parking space
D. Using the rear door of a hatchback car
242. You wish to make a right turn ahead. Why should you take up the correct position in good time?
A. To allow other drivers to pull out in front of you
B. To help other road users know what you intend to do
C. To give a better view into the road that you are joining
D. To allow other drivers to pass you on the right
243. Why would a pedestrian dress their dog in a yellow or burgundy coat; what are they warning you about?
A. Elderly
B. Dog training
C. Colour blind
D. Deaf
244. You should never reverse
A. For longer than necessary
B. At night
C. Into a side road
D. On a main road
245. You are driving on a clear night. There is a steady stream of oncoming cars. The national speed limit applies. Which lights should you use?
A. Dipped headlights
B. Full beam headlight
C. Fog lights
D. Sidelights
Dip your headlights when meeting other vehicles and cyclists. high beam may dazzle the other drivers and cause danger
246. How should you react to drivers who appear to be inexperienced?
A. Flash your headlights to indicate that it is safe for them to proceed
B. Overtake them as soon as possible
C. Be patient and prepare for them to react more slowly
D. Sound your horn and warn them of your presence
247. When being followed by an ambulance showing a flashing blue light you should:
A. Pull over as soon as safely possible to let it pass
B. Brake harshly and immediately stop in the road
C. Accelerate fast to get away from it
D. Maintain your speed and course
248. You are driving at the legal speed limit. A vehicle comes up quickly behind, flashing its headlights. You should:
A. Allow the vehicle to overtake
B. Touch the brakes to show your brake lights
C. Accelerate to make a gap behind you
D. Maintain your speed to prevent the vehicle from overtaking
249. What do child locks in a vehicle do?
A. Lock the seat belt buckles in place
B. Stop children from opening rear doors
C. Stop the rear seats from tipping forward
D. Lock the rear windows in the up position
250. Which of the following should you do before stopping?
A. Sound the horn
B. Flash your headlights
C. Use the mirrors
D. Select a higher gear
251. A provisional licence holder must not drive a motorcar
A. Alone
B. With passengers in the back
C. At night
D. On a dual carriageway
252. You are turning left on a slippery road. The back of your vehicle slides to the right. You should
A. Brake firmly and steer to the left
B. Brake firmly and not turn the steering wheel
C. Steer carefully to the right
D. Steer carefully to the left
253. Who is especially in danger of not being seen as you reverse your car?
A. Children
B. Car drivers
C. Motorcyclists
D. Cyclists
254. Rapid acceleration and heavy braking can lead to
A. Increased fuel consumption
B. Reduced pollution
C. Reduced exhaust emissions
D. Increased road safety
255. When correcting a rear-wheel skid you should
A. Brake sharply
B. roll with it
C. Steer into the skid
D. Steer away from the skid
256. A cycle lane is marked by a solid white line. You must not drive or park in it
A. During its period of operation
B. At any time
C. During the rush hour
D. If a cyclist is using it
257. You MUST wear glasses or contact lenses when driving on public roads if:
A. You cannot read a vehicle number plate from distance of 20.5 meters (67 feet) without them
B. You cannot read a vehicle number plate from a distance of 36 meters (120 feet) without them
C. There is an eyesight problem in your family
D. You are the holder of an orange badge
258. You are waiting to emerge left from a minor road. A large vehicle is approaching from the right. You have time to turn, but you should wait. Why?
A. The large vehicle can easily hide an overtaking vehicle
B. The large vehicle can turn suddenly
C. The large vehicle is difficult to steer in a straight line
D. The large vehicle can easily hide vehicles from the left
259. To correct a rear-wheel skid you should
A. Steer into it
B. Apply your handbrake
C. Not steer at all
D. Steer away from it
260. The road is wet and slippery. Why might a motorcyclist steer round drain covers on a bend?
A. To avoid splashing pedestrians on the pavements
B. To prevent the motorcycle sliding on the metal drain covers
C. To avoid puncturing the tyres on the edge of the drain covers
D. To help judge the bend using the drain covers as marker points
261. After how many years does a car first need a MOT certificate?
A. One year
B. Four years
C. Three years
D. Two years
262. You are parking on a two-way road at night. The speed limit is 40 mph. You should park on the
A. Left with no lights on
B. Left with parking lights on
C. Right with dipped headlights on
D. Right with parking lights on
263. Motorcyclists often look round over their right shoulder just before turning right. This is because
A. Motorcycles do not have mirrors
B. They need to check for traffic in their blind area
C. They need to listen for following traffic
D. Looking around helps them balance as they turn
264. What is the most common reason a car skids?
A. Driver error
B. Pedestrians
C. Worn tyres
D. Other vehicles
265. What is the legal minimum insurance cover you must have to drive on public roads?
A. Third party, fire and theft
B. Personal injury cover
C. Third party only
D. Fully comprehensive
266. When must you stop at this junction?
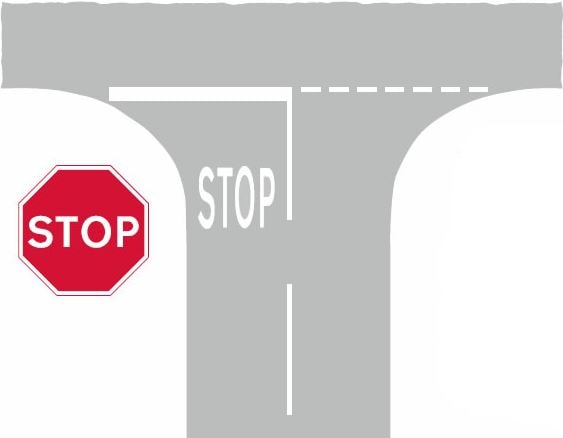
A. Only when the area is busy
B. At all times
C. During rush hours only
D. When turning right only
Motorists must stop behind the line at a junction where a stop sign is in place with a solid white line. It is law that a driver must stop at least once before the line and wait for a safe gap before proceeding.
Do cyclists have to stop at stop signs
The Highway Code states to cyclists ‘You MUST obey all traffic signs and traffic light signals’. Like motorists, cyclists must also stop at stop signs.
267. When about to overtake a long vehicle or lorry you should:
A. Drive close to the lorry in order to pass more quickly
B. Sound the horn to warn the driver that you are there
C. Stay well back from the lorry to obtain a better view
D. Flash your lights and wait for the driver to signal when it is safe
268. How can you use the engine of your vehicle to control your speed?
A. By selecting neutral
B. By selecting reverse gear
C. By changing to a higher gear
D. By changing to a lower gear
269. You should never wave or urge people across at pedestrian crossing because
A. It is safer for you to carry on
B. They may not be ready to cross
C. They may not be looking
D. There may be another vehicle coming
Be patient and stay safe, not only for yourself but also for other road users
270. Why should you make sure that you have cancelled your indicators after turning?
A. To avoid flattening the battery
B. To avoid misleading other road users
C. To avoid dazzling other road users
D. To avoid damage to the indicator relay
271. You need to top up your battery. What level should you fill to?
A. Just below the cell plates
B. Half-way up the battery
C. Just above the cell plates
D. The top of the battery
272. You are driving a slow moving car on a narrow road. When traffic wishes to overtake you should
A. Put your hazard warning lights on
B. Pull in safely as soon as you can do so
C. Stop immediately and wave it on
D. Take no action
Safety is 1st priority, and at the same time try to keep a smooth traffic flow
273. What does tailgating mean?
A. When stationary vehicles are too close in a queue
B. When a vehicle delivering goods has its tailgate down
C. When a driver is following another vehicle too closely
D. When a vehicle is with its back doors open
274. A car pulls out in front of you at a junction. What should you do?
A. Swerve past it and blow your horn
B. Accelerate past it immediately
C. Flash your headlights and drive up close behind
D. Slow down and be ready to stop
Do not overtake other vehicles when approaching a junction.
275. If you are on good, dry road surface and your vehicle has good brakes and tyres, what is the overall stopping distance at 48 kph?
A. 36 meters (118 feet)
B. 23 meters (75 feet)
C. 96 meters (315 feet)
D. 53 meters (174 feet)
276. You see this line across the road at the entrance to a roundabout. What does it mean?

A. Traffic from the left has right of way
B. You have right of way
C. Give way to traffic from the right
D. Stop at the line
The broken white line is a reminder to give way to traffic from the right at roundabouts. You can expect to find these at larger roundabouts.
277. The purpose of a catalytic converter is to
A. Increase acceleration
B. Reduce toxic exhaust gases
C. Reduce oil consumption
D. Reduce fuel consumption
278. Anti-lock brakes reduce the chances of a skid occurring particularly when:
A. Breaking in an emergency
B. Driving on good road surfaces
C. Driving down steep hills
D. Breaking during normal driving
279. You are testing the suspension of your car. You notice that your vehicle keeps bouncing when you press down on the front wing. What does this mean?
A. Steering wheel not located centrally
B. Worn shock absorbers
C. Tyres under-inflated
D. Worn tyres
280. An injured motorcyclist is lying unconscious in the road. You should
A. Move the person off the road
B. Remove the leather jacket
C. Remove the safety helmet
D. Seek medical assistance
281. Following a collision someone has suffered a burn. The burn needs to be cooled. What is the shortest time it should be cooled for?
A. 5 minutes
B. 15 minutes
C. 20 minutes
D. 10 minutes
282. How can you help to prevent your car radio from being stolen?
A. Park in an unlit area
B. Install a security-coded radio
C. Park near a busy junction
D. Hide the radio with a blanket
283. If you start to feel tired whilst driving you should
A. Decrease your speed
B. Increase your speed to reduce your journey time
C. Stop at a safe place and rest
D. Turn on the radio and listen to loud music
284. At the scene of an accident you should:
A. Go to those casualties who are screaming
B. Not put yourself at risk
C. Leave vehicle engines switched on
D. Pull everybody out of their vehicles
285. You are following a motorcyclist on an uneven road. You should:
A. Allow extra room in case they swerve to avoid pot-holes
B. Allow the same room as normal because motorcyclists are not affected by road surfaces
C. Allow less room to ensure that you can be seen in their mirrors
D. Overtake immediately
286. You are driving at night with full-beam headlights on. A vehicle is overtaking you. You should dip your lights
A. Some time after the vehicles has passed you
B. Before the vehicles starts to pass you
C. As soon as the vehicle passes you
D. Only if the other driver dips his headlights
287. Which vehicle may have to use a different course to normal at roundabouts?
A. Estate car
B. Long vehicle
C. Sports car
D. Van
288. You stop for pedestrians waiting to cross at a zebra crossing. They do not start to cross. What should you do?
A. Carry on
B. Be patient and wait
C. Wave then to cross
D. Sound your horn
289. When following a vehicle on a wet road you should leave a time gap of at least?
A. 3 seconds
B. 4 seconds
C. 2 seconds
D. 1 second
290. Motorcycles ride in day light with their headlights switched on because
A. There are speed humps ahead
B. It is legal requirement
C. They need to be seen
D. There is a speed trap ahead
291. You are driving in town. There is a bus at the bus stop on the other side of the road. Why should you be careful?
A. The bus may remain stationary
B. The bus may move off suddenly
C. Pedestrians may come from behind the bus
D. The bus may have broken down
292. In which of these following situations should you avoid overtaking?
A. Just after a bend
B. In a one-way street
C. On a 30 mph road
D. Approaching a dip in the road
Try to avoid overtaking when approaching a bend, dip, zebra crossing, road junction, on a bridge or the peak of a mountain.
293. Where may you overtake on a one-way Street?
A. Either on the right or the left
B. Overtaking is not allowed
C. Only on the left-hand side
D. Only on the right-hand side
294. Using rear fog lights in clear daylight or tunnels will:
A. Make following drivers keep back
B. Dazzle others drivers
C. Give extra protection
D. Be useful when towing a trailer
295. You are about to drive home. You cannot find the glasses you need to wear when driving. You should:
A. Drive home slowly, keeping to quite roads
B. Find a way of getting home without driving
C. Drive home at night
D. Borrow a friend’s glasses and drive home
296. In freezing conditions you should expect stopping distances to increase by up to
A. Four (4) times
B. Ten (10) times
C. Seven (7) times
D. Five (5) times
297. What does this sign mean?

A. End of narrow bridge
B. Road narrows
C. End of dual carriageway
D. Tall bridge
298. When being followed by an ambulance showing a flashing blue beacon you should
A. Pull over as soon as safely possible to let it pass
B. Maintain your speed and course
C. Accelerate hard to get away from it
D. Brake harshly and immediately stop in the road
299. You are travelling at the legal speed limit. A vehicle comes up quickly behind, flashing its headlights. You should
A. Accelerate to make a gap behind you
B. Touch the brakes sharply to show your brake lights
C. Maintain your speed to prevent the vehicle from overtaking
D. Allow the vehicle to overtake
300. What lights and why must you put them on when going through a tunnel?
A. No lights are necessary as tunnels have their own lighting.
B. Dipped-beam to help you see and also be clearly seen by others.
C. Main-beam to see clearly where you are going.
D. Hazard warning lights so nobody drives too near.
E. Dipped-beam and front and/or rear Fog lights to see and be seen clearly.
301. What is the national speed limit for towing a trailer on a motorway?
A. 40 mph
B. 50 mph
C. 60 mph
D. 70 mph
302. In windy conditions you need to take extra care when
A. Using the brakes
B. Making a hill start
C. Passing pedal cyclists
D. Turning into a narrow road
303. You are about to drive home but you can't find the glasses you need to wear. You should:
A. Only drive on minor roads
B. Drive home at night so that the lights will help you
C. Drive home without going faster than 30 mph
D. Find a way of getting home without driving
304. Immediately after joining a motorway you should:
A. Move to the centre lane
B. Move to the right hand lane
C. Try to overtake
D. Keep in the left lane to get used to the speed
305. You should only use a mobile phone when
A. Driving an automatic vehicle
B. Driving at less than 30 mph
C. Receiving a call
D. Suitably parked
306. Anti-lock brakes are most useful when you are
A. Driving on worn tyres
B. Braking gently
C. Braking excessively
D. Driving normally
307. Why are mirrors often slightly curved (convex)?
A. They make it easier to judge the speed of following traffic
B. They totally cover blind spots
C. They make following traffic look bigger
D. They give a wider field of vision
308. What does this sign mean?

A. Ancient monument ahead
B. Tunnel ahead
C. Low bridge ahead
D. Accident black spot ahead
309. You are entering an area of road works. There is a temporary speed limit displayed. You must
A. Accept the speed limit as advisable
B. Not exceed the speed limit
C. Obey the limit except for overnight
D. Obey the limit only during rush hour
310. Objects or articles hanging from your interior mirror may
A. Help your concentration
B. Distract your attention
C. improve your view
D. Improve your driving
311. What is the main cause of skidding?
A. The weather
B. Damaged brakes
C. Driving too fast
D. The driver
312. At a crossroads there are no signs or road markings. Two vehicles approach. Which has priority?
A. The vehicle on the widest road
B. The vehicle the fastest
C. Neither vehicle
D. Vehicles approaching from the right
313. You should never wave people across at pedestrian crossings because
A. There may be another vehicle coming
B. They may not be looking
C. They may not be ready to cross
D. It is safer for you to carry on
314. You are driving down a long steep hill. You suddenly notice that your brakes are not working as well as normal. What is the usual cause of this?
A. The brakes overheating
B. Badly adjusted
C. Air in the brake fluid
D. Oil on the brakes
315. Which of the following are at greatest risk from other road users?
A. Motorcycles
B. Lorry drivers
C. Busy bus drivers
D. Learner car drivers
316. What are the maximum national speed limits for cars and motorcycles in built-up areas and elsewhere?
A. 50kph and 80kph
B. 30mph and 70mph
C. 40kph and 70kph
D. 45mph and 100mph
317. You can use the engine of your vehicle as a brake by
A. By travelling with the clutch pressed down
B. By selecting fifth gear
C. By turning the engine off
D. By selecting a lower gear
318. For which of these must you show on your motor insurance certificate?
A. When having an MOT inspection
B. When buying or selling a vehicle
C. When you are taking your driving test
D. When a police office asks for it
319. You wish to overtake a long, slow moving vehicle or lorry on a busy road with oncoming traffic. You should:
A. Follow it closely and keep moving out to see the road ahead
B. Stay behind until the driver waves you past
C. Keep well back until you can see that it is clear
D. Flash your headlights for the oncoming traffic to give way
320. Any load that is carried on a roof rack should be
A. Visible in your exterior mirror
B. Loaded towards the rear of the vehicle
C. Securely fastened when driving
D. Covered with plastic sheeting
321. At the scene of an accident you have to treat someone for shock. What should you do?
A. Keep reassuring them until qualified help arrives
B. Give them liquids to drink
C. Try and cool them down
D. Sing to them
322. This marking appears on the road just before a
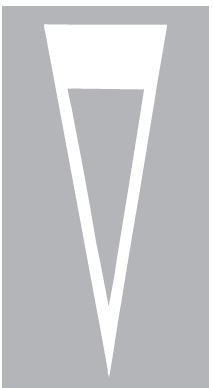
A. No through road sign
B. Stop sign
C. Give way sign
D. No entry sign
323. For a driver, what doe the term Blind Spot mean?
A. An area immediately behind the car
B. The area covered by your left mirror
C. The area covered by the rear view mirror
D. An area not seen in your mirrors
324. At toucan crossings, apart from pedestrians you should be aware of
A. Buses pulling out
B. Emergency vehicles emerging
C. Cyclists riding across
D. Trams crossing in front
325. You are turning left on a slippery road. The back of your vehicle slides to the right. You should:
A. Brake firmly and not turn the steering wheel
B. Steer carefully to the left
C. Brake firmly and steer to the left
D. Steer carefully to the right
326. You are approaching a zebra crossing. Pedestrians are waiting to cross. You should:
A. Wave at them to cross the road
B. Give way to elderly and infirm only
C. Slow down and prepare to stop
D. Use your headlights to indicate they can cross
327. You should ONLY use a mobile or cellular phone when:
A. Driving an automatic vehicle
B. Suitably parked
C. Receiving a call
D. Driving at less than 30 mph
Using a mobile phone while driving is dangerous, since your attention is diverted away from the road
328. You will use more fuel if your tyres are
A. Of different makes
B. New and hardly used
C. Under-inflated
D. Over-inflated
329. What do these solid double white centre line road markings mean?

A. Lines on the road just to mark the lanes and guide traffic flows, which have no legal or safety implications.
B. Continuous solid double white line (Centre line) which vehicles must not drive over, across or astride except to enter a side road, unless prohibited from doing so by appropriate signage.
C. Central limit of dual carriageway and may be crossed only when overtaking.
D. No stopping or parking permitted.
330. A roof rack that is fitted to your car will:
A. Improve the road handling
B. Make your car go faster
C. Reduce fuel consumption
D. Increase fuel consumption
331. The road is icy. You should drive slowly
A. With your left foot on the brake
B. In the lowest gear possible
C. With the handbrake partly on
D. In the highest gear possible
332. You see this sign ahead of you. It means:

A. Start to slow down to 30 kph after passing it
B. You are leaving the 30 kph speed limit area
C. The minimum speed limit ahead is 30 kph
D. Do not exceed 30 kph after passing it
333. On a road where trams operate, which of these vehicles will be most at risk from tram rails?
A. Buses
B. Cycles
C. Lorries
D. Cars
334. Which type of crossing can detect when people are on them?
A. Puffin
B. Zebra
C. Pelican
D. Toucan
335. Signals are normally given by direction indicators and
A. Interior lights
B. Sidelights
C. Brake lights
D. Fog lights
336. You are carrying a child in your car. They are under three years of age. Which of these is a suitable restraint?
A. An adult lap belt
B. A child seat
C. An adult seat belt
D. An adult holding a child
337. What is the maximum number of penalty points that will automatically disqualify a driver who holds a provisional driving licence?
A. 12 points at any time during a 3 year period
B. 10 points during any one year period
C. 4 points a year over a 3 year period
D. 18 points over a two year period
E. 15 points over a five 5 year period
338. You take the wrong route and find you are on a one-way street. You should:
A. Reverse into a driveway
B. Turn round in a side road
C. Continue to the end of the road
D. Reverse out of the road
339. Coasting your vehicle whilst driving will:
A. Increase the control you have over the vehicle
B. Reduce the vehicle's braking distance
C. Make the car use more fuel
D. Decrease the control you have over the vehicle
340. Using a hands-free phone is likely to
A. Increase your concentration
B. Divert your attention
C. Improve your safety
D. Reduce your view
Using a mobile phone while driving is dangerous. your attention should not be diverted away from the road
341. Using rear fog lights in clear daylight will
A. Dazzle other drivers
B. Give extra protection
C. Make following drivers keep back
D. Be useful when towing a trailer
342. Why should you always reduce your speed when travelling in fog?
A. It is more difficult to see events ahead
B. The brakes do not work as well
C. You will be dazzled by oncoming headlights
D. The engine will take longer to warm up
343. When MUST you use dipped headlights during the day?
A. When parking
B. Along narrow streets
C. In poor visibility
D. All the time
344. You are on a well-lit motorway at night. You must
A. Use your headlights only in bad weather
B. Use only your sidelights
C. Always use your headlights
D. Always use your rear fog lights
345. A driver's behaviour has upset you. It may help if you
A. Shout abusive language
B. Gesture to them with your hand
C. Stop and take a break
D. Follow their car, flashing your headlights
346. If you cannot see clearly behind when reversing, what should you do?
A. Ask someone to guide you
B. Open the door and look behind
C. Open your window to look behind
D. Look in the nearside mirror
347. What does this sign mean?

A. Crossroads
B. Roundabout
C. No entry
D. No stopping
348. When emerging from junctions, which is most likely to obstruct your view?
A. Interior mirror
B. Steering wheel
C. Windscreen pillars
D. Windscreen wipers
349. An elderly person's driving ability could be affected because they may be unable to
A. Give signals correctly
B. Understand road signs
C. Obtain car insurance
D. React very quickly
350. You are in a line of traffic. The driver behind you is following very closely. What action should you take?
A. Move over to a position just left of the centre line of the road
B. Signal left and wave the following driver past
C. Slow down, gradually increasing the gap between you and the vehicle in front
D. Ignore the following driver and continue to drive within the speed limit
Allow room for the vehicle to overtake
351. You wish to turn right ahead. Why should you take up the proper position in good time?
A. To allow other drivers to pull out in front of you
B. To allow drivers to pass you on the right
C. To give a better view into the road that you are joining
D. To help other road users know what you intend to do
It is essential and important to let others know your intension as early as possible to prevent wrong perception and accidents
352. To help the environment you should NOT:
A. Walk, cycle, or use public transport
B. Remove your roof rack when unloaded
C. Use your car for very short journeys
D. Empty the boot of unnecessary weight
353. As soon as you join a dual carriageway you should normally:
A. Position your vehicle in the centre lane
B. Keep in the left lane
C. Readjust your mirrors
D. Try to overtake
354. Which of the following is the main cause of rear-end collisions?
A. A wet road surface
B. Pedestrians crossing the road unexpectedly
C. Traffic lights
D. Driving too close to the vehicle in front
355. At an incident it is important to look after any casualties. When the area is safe you should
A. Keep them in the vehicle
B. Give them a drink
C. Give them something to eat
D. Get them out of the vehicle
356. You are at a junction controlled by traffic lights. When should you NOT proceed at green?

A. When your exit from the junction is blocked
B. When pedestrians are waiting to cross
C. When you think the lights may be about to change
D. When you intend to turn right
357. In good conditions, what is the typical stopping distance at 70 mph?
A. 53 meters (175 feet)
B. 96 meters (315 feet)
C. 73 meters (240 feet)
D. 60 meters (197 feet)
358. Vehicles fitted with an anti-lock brake system
A. Can be steered while you are braking
B. Are impossible to skid
C. Accelerate much faster
D. Are not fitted with a handbrake
359. A newly qualified driver must
A. Display green L-Plates
B. Have valid motor insurance
C. Not exceed 40 mph for 12 months
D. Be accompanied on a motorway
360. When turning your car in the road, you must:
A. Overhang the kerb
B. Check all around for other road users
C. Keep your hand on the handbrake
D. Use an available driveway
Look out for other road users when turning, especially pedestrians
361. Which type of vehicle is most affected by strong winds?
A. Tanker
B. Motorcycle
C. Car
D. Tractor
362. Motorcars must first have an MOT certificate when they are
A. Five (5) years old
B. One (1) year old
C. Three (3) years old
D. Seven (7) years old
363. You have driven through a flood. What is the first thing you should do?
A. Check your exhaust
B. Stop and dry the brakes
C. Stop and check the tyres
D. Test your brakes
364. You are approaching an unmarked crossroads. How should you deal with this type of junction?
A. Accelerate looking to the left
B. Slow down and look both ways
C. Slow down and keep to the right
D. Accelerate and keep to the middle
365. Some two-way roads are divided into three lanes. Why are these particularly dangerous?
A. Traffic can travel faster in poor weather conditions
B. Traffic uses the middle lane for emergencies only
C. Traffic can overtake on the left
D. Traffic in both directions can use the middle lane to overtake
366. You are following a large lorry on a wet road. Spray makes it difficult to see. You should:

A. Put your headlights on full beam
B. Drop back until you can see better
C. Keep close to the lorry, away from the spray
D. Speed up and overtake quickly
367. Front and rear fog lights MUST be:
A. Switched of if visibility is not seriously reduced
B. Used outside built up areas only
C. Switched off in night-time fog
D. Connected to an audible warning signal
368. You want to turn from a junction but your view is partly restricted by parked vehicles. What should you do?
A. Move out quickly, but be prepared to stop
B. Stop, get out and look along the main road to check
C. Stop, then move slowly forward until you have a clear view
D. Sound your horn and pull out if there is no reply
369. On a three-lane motorway which lane should you normally use?
A. Centre
B. Left
C. Either the right or centre
D. Right
370. You are dazzled at night by the lights of the vehicle behind you. You should:
A. Set your mirror to dazzle the other driver
B. Set your mirror to anti-dazzle
C. Brake sharply to a stop
D. Switch your rear lights on and off
371. At night, you are dazzled by headlights coming towards you. You should:
A. Slow down or stop
B. Switch on your main beam headlights
C. Put your hand over your eyes
D. Pull down your sun visor
372. Fog lights should be used ONLY when
A. Visibility is seriously reduced
B. Driving after midnight
C. In very light rain
D. Daylight is fading
373. You are about to reverse into a side road and a pedestrian wishes to cross behind you. You should:
A. Give way to the pedestrian
B. Wave to the pedestrian to stop
C. Wave to the pedestrian to cross
D. Reverse before the pedestrian starts to cross
374. What is the maximum speed limit in a built up area unless indicated otherwise?
A. 60mph
B. 50mph
C. 40mph
D. 30mph
375. Motorcyclists are particularly vulnerable
A. When moving off
B. On dual carriageways
C. When approaching junctions
D. On motorways
376. Motorcyclists are more at risk to be injured from other road users because they
A. Are less experienced that other drivers
B. Are more difficult to see than other drivers
C. Are always faster than other drivers
D. Are more likely to break down than other motorists
377. You are approaching a right-hand bend. You should:
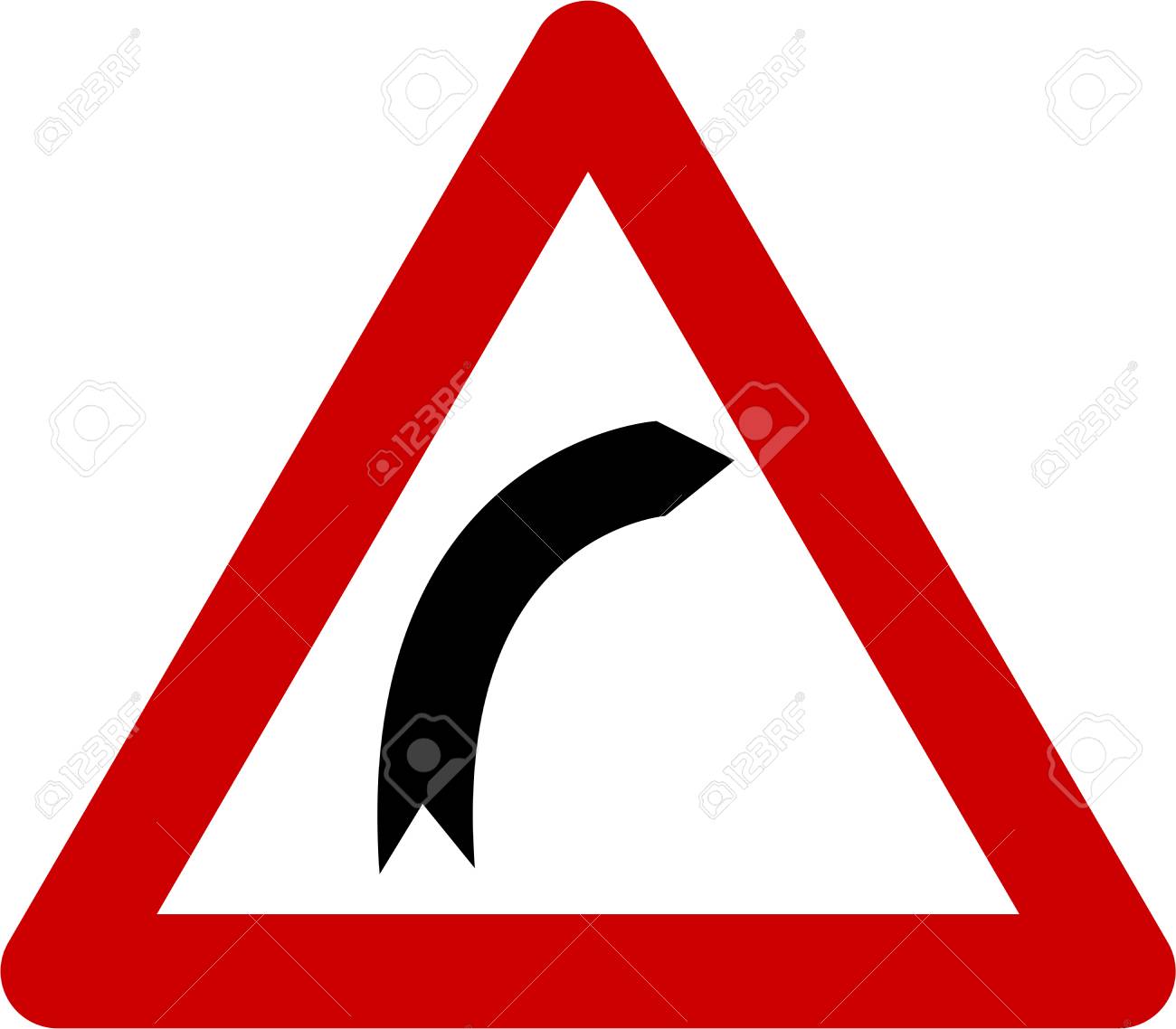

A. Keep well to the right to avoid anything in the gutter
B. Keep well to the left as it makes the bend faster
C. Keep well to the left for a better view around the bend
D. Keep well to the right to make the bend less sharp
378. How should you overtake horse riders?
A. Drive slowly and leave plenty of room
B. Speed is not important but allow plenty of room
C. Use your horn just once to warn them
379. What is the meaning of this sign?
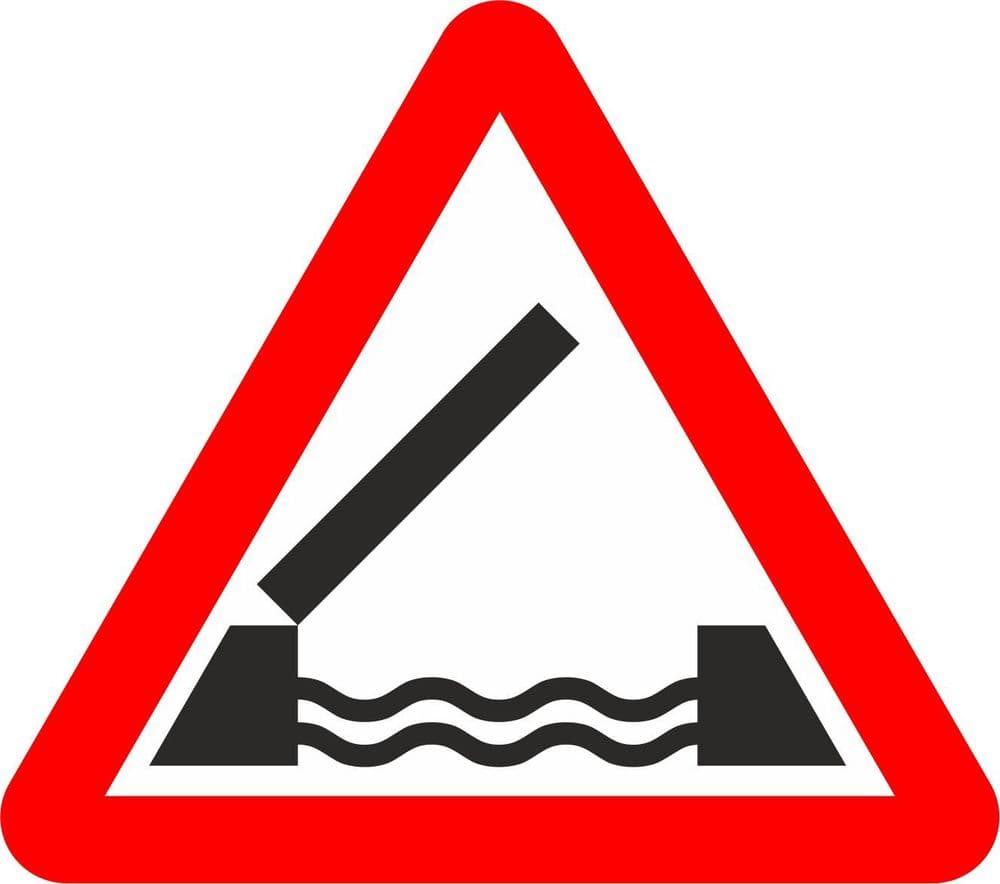

A. Humpback bridge ahead
B. Toll bridge ahead
C. Road ahead closed
D. Opening or swing bridge ahead
380. A learner driver you are following stalls at a junction. What should you do?
A. Shout instructions
B. Sound your horn and flash your lights
C. Steer around them and drive on
D. Be patient and wait for them to move on
381. What is the meaning of this sign?

A. Minimum speed 20 mph
B. Entry into a 20 mph zone
C. End of a 20 mph zone
382. You may only enter a box junction when:

A. There are less than two vehicles in front of you
B. The traffic lights show green
C. You need to turn left
D. Your exit road is clear
383. To answer your mobile phone when driving, you should:
A. Stop in a proper and convenient place
B. Slow down and allow others to overtake
C. Reduce your speed wherever you are
D. Keep the call time to a minimum
384. What is the most likely cause of high fuel consumption?
A. Harsh braking and accelerating
B. Poor steering control
C. Accelerating around bends
D. Staying in high gears
385. Why should you particularly look for motorcyclists and cyclists at any junction?
A. They are harder to see
B. They might not see you turn
C. They nay want to turn into the side road
D. They may slow down to let you turn
386. Unbalanced wheels on a car may cause
A. Poor acceleration
B. Poor braking
C. The tyres to wear out
D. The steering to vibrate
387. Which one is adversely affected if the tyres are under-inflated?
A. Accelerating
B. Braking
C. Changing gear
D. Parking
388. A provisional licence holder must not drive a motor car
A. With passengers
B. At night
C. Alone
D. On a dual carriageway
389. At a crossroads there are no signs or road markings. Two vehicles approach. Which has priority?
A. Oncoming vehicles turning right
B. The vehicle travelling the fastest
C. Vehicles approaching from the right
D. Neither of the vehicles
390. It is very windy. You are behind a motorcyclist who is overtaking a high-sided vehicle. What should you do?
A. Overtake the motorcyclist immediately
B. Keep well back
C. Keep close to the motorcyclist
D. Stay level with the motorcyclist
391. At an accident you suspect a casualty has back injuries. The area is safe. You should:
A. Offer them a drink
B. Raise their legs
C. Offer them a cigarette
D. Not move them
392. You should NEVER attempt to overtake a cyclist
A. Just before you turn left
B. On a one-way street
C. Just before you turn right
D. On a dual carriageway
393. You are parked in a busy high street. What is the safest way to turn your vehicle around so you can go the opposite way?
A. Do a U-turn
B. Get someone to stop the traffic
C. Drive into a side road and reverse into the main road
D. Find a quiet side road to turn around in
394. You are driving on a multi-lane carriageway. By mistake, you go past the exit that you wanted to take. You should:

A. Carefully reverse on the hard shoulder
B. Carefully reverse in the left-hand lane
C. Carry on to the next exit
D. Make a U-turn at the next gap in the central reservation
395. You are driving in fog. Why should you keep well back from the vehicle in front?

A. In case its brake lights dazzle you
B. In case its fog lights dazzle you
C. In case it changes direction suddenly
D. In case it stops suddenly
396. When driving through a ford or floodwater, what gear should you be in?
A. Third
B. First or second
C. Fourth
D. Fifth
397. You are waiting to emerge from a minor road. A large vehicle is approaching from the right. You have time to turn, but you should wait. Why?
A. The large vehicle can easily hide an overtaking vehicle
B. The large vehicle can easily hide vehicles from the left
C. The large vehicle is difficult to steer in a straight line
D. The large vehicle can turn suddenly
398. How can you use the engine of your vehicle as a brake?
A. By changing to a higher gear
B. By changing to a lower gear
C. By selecting reverse gear
D. By selecting neutral gear
399. What does a sign with a brown background show?

A. Minor routes
B. Tourist directions
C. Primary roads
D. Motorway routes
400. You are driving in very wet weather. Your vehicle begins to slide. This affect is called:
A. Aquaplaning
B. Weaving
C. Hosing
D. Fading
401. A long, heavily laden lorry is taking a long time to overtake you. What should you do?
A. Slow down
B. Hold you speed
C. Change direction
D. Speed up
402. You are driving on a dual carriageway and the car ahead shows its hazard lights for a short time. This tells you that:
A. The other car is going to change lanes
B. Traffic ahead is slowing or stopping suddenly
C. There is a police speed check up ahead
D. The driver wants you to overtake
403. You see this sign ahead. You should expect the road to:

A. Bend sharply to the right
B. Bend sharply to the left
C. Go steeply downhill
D. Go steeply downhill
404. Freezing conditions will affect the distance it takes you to come to a stop. You should expect stopping distances to increase by up to
A. Ten (10) times
B. Three (3) times
C. Two (2) times
D. Five (5) times
405. At a pelican crossing the flashing amber light means you MUST
A. Give way to pedestrians waiting to cross
B. Stop and wait for the red light
C. Stop and wait for the green light
D. Give way to pedestrians already on the crossing
406. The most important reason for having a properly adjusted head restraint is to
A. Make you more comfortable
B. Help you to relax
C. Help you to maintain your driving position
D. Help you to avoid neck injury
407. What is the nearest you can park your vehicle to a junction?
A. 20 meters
B. 22 meters
C. 15 meters
D. 10 meters
408. When may you use hazard warning lights?
A. To park alongside another car
B. When you are being towed
C. To park on double yellow lines
D. When you have broken down
409. Road humps, chicanes, and road narrowing's are
A. At toll-bridge approaches only
B. Used to increase traffic speed
C. Always at major road works
D. Traffic calming measures
410. The driver of the car in front is giving this signal. What does it mean?

A. The drivers intends to turn left
B. The driver is slowing down
C. The driver intends to turn right
D. The driver wishes to overtake
411. You are driving in heavy rain. Your steering suddenly becomes very light. You should
A. Ease off the accelerator
B. Steer towards the side of the road
C. Brake firmly to reduce speed
D. Apply gentle acceleration
412. What does the sign mean?
A. No pedestrians
B. Route for pedestrians
C. Pedestrians in the road ahead
D. Pedestrian crossing
413. You see this sign ahead. It means:

A. Waiting restrictions apply
B. No stopping
C. No entry
D. National speed limit applies
414. Coasting the car:
A. Reduces the driver’s control
B. Makes steering easier
C. Improves the driver’s control
D. Uses more fuel
415. You are driving behind a long vehicle. It approaches a crossroads and signals left, but moves out to the right. You should:-
A. Assume the signal is wrong and it is really turning right
B. Overtake as it starts to slow down
C. Get closer in order to pass it quickly
D. Stay well back and give it room
416. You are driving in traffic at the speed limit for the road. The driver behind is going to overtake. You should:
A. Move closer to the car ahead, so the driver behind has no room to overtake
B. Keep a steady course and allow the driver behind to overtake
C. Accelerate to get away from the driver behind
D. Wave the driver behind to overtake when it is safe
Safety is the 1st priority, at the same time try to keep a smooth traffic flow and give room for others
417. You are waiting in a traffic queue at night. To avoid dazzling the drivers behind, you should:
A. Apply the footbrake only
B. Switch off your headlights
C. Use both the handbrake and footbrake
D. Apply the handbrake only
The brake light will be switched on when using the footbrake
418. A pedestrian with a white stick and red band is
A. Deaf and dumb
B. Over 65 years old
C. Blind only
D. Deaf and blind
419. You arrive at the scene of a motorcycle accident and the rider is injured. When should the helmet be removed?
A. Always straight away.
B. Only when it is essential.
C. Always, unless they are in shock.
D. Only when the motorcyclist asks
It is important not to remove their helmet unless it is necessary to do so to keep them alive
420. You are on a busy main road and find that you are in a wrong direction. What should you do?
A. Turn round in a side road
B. Turn into a side road on the road on the right and reverse into the main road.
C. Make a ‘three point’ turn in the main road
D. Make a U-turn in the main road
421. What is the safest way to use a mobile phone in a car?
A. Drive slowly on a quiet road
B. Direct your call thought the operator
C. Find a suitable place to stop
D. Use hands-free equipment
Using a mobile phone while driving will make you less concentrate on the road, it is a dangerous practice
422. Planning your journey to avoid busy times has a number of advantages. One of these is
A. Your journey will take longer
B. Your stress levels will be greater
C. You will cause more pollution
D. You will have a more pleasant journey
423. What does this sign mean?

A. Two-way traffic ahead
B. You have priority over vehicles from the opposite direction
C. No overtaking
D. You are entering a one way street
424. How does alcohol affect your driving?
A. It improves your coordination
B. It reduces your concentration
C. It speeds up your reactions
D. It increases your awareness
425. You are driving on an icy road. How can you avoid wheel spin?
A. Use the handbrake if the wheels start to slip
B. Drive in a low gear at all times
C. Drive at a slow speed in as high gear as possible
D. Brake gently and repeatedly
426. You want to turn right from a main road into a side road. Just before you turn you should
A. Select first gear
B. Stop and set the handbrake
C. Cancel your right-turn signal
D. Check for traffic overtaking on your right
427. What is the nearest you may park to a junction?
A. 12 meters (39 feet)
B. 10 meters (32 feet)
C. 15 meters (49 feet)
D. 20 meters (66 feet)
This is to allow drivers emerging from, or turning into, the junction a clear view of the road they are joining.
428. A flashing green beacon on a vehicle means
A. Police on non-urgent duties
B. Doctor on an emergency call
C. Road safety patrol operating
D. Gritting in progress
429. You have driven your car through a flood. What is the first thing you should do?
A. Stop and check the tyres
B. Stop and dry the brakes
C. Test your brakes
D. Switch on your windscreen wipers
430. What does this sign mean?
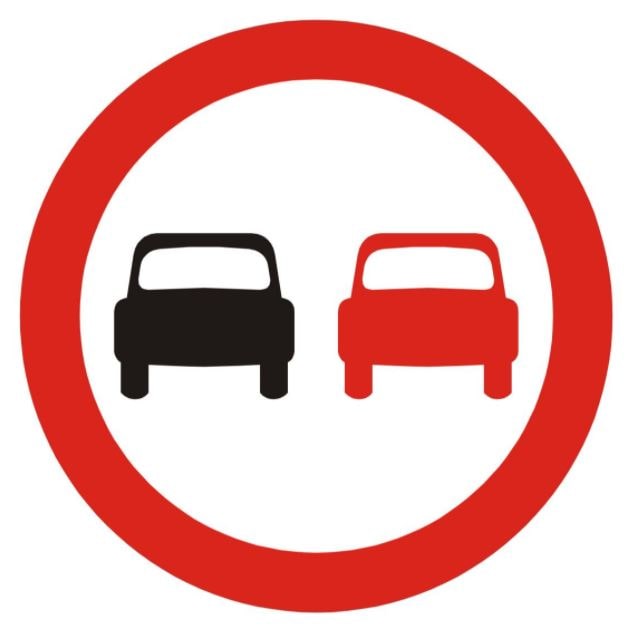

A. Two-way traffic
B. You have priority
C. No overtaking
D. No motor vehicles
431. What is the safest way to us a mobile phone in you vehicle?
A. Direct your call through the operator
B. Drive slowly on a quiet road
C. Use hands-free equipment
D. Find a suitable place to stop
432. You are approaching two cyclists. They approach a roundabout in the left-hand lane. In which direction should you expect the cyclists to go?
A. Right
B. Any direction
C. Left
D. Straight ahead
433. Why are vehicles fitted with rear fog lights?
A. To be seen when driving at high speed
B. To warn drivers following closely to drop back
C. To make them more visible in thick fog
D. To use if broken down in a dangerous position
434. You intend to turn right into a side road. Just before turning you should check for motorcyclists who may be:
A. Emerging from the side road
B. Overtaking on your left
C. Overtaking on your right
D. Following you closely
435. You intend to turn right into a side road. Just before turning you should check for motorcyclists who might be
A. Emerging from the side road
B. Following you closely
C. Overtaking on your right
D. Overtaking you on the left
436. Someone is waiting to cross at a zebra crossing. They are standing on the pavement. You should normally:
A. Go on quickly before they step onto the crossing
B. Stop, let them cross, wait patiently
C. Ignore them as they are still on the pavement
D. Stop before you reach the zigzag lines and let them cross
437. When are you permitted to exceed the maximum speed limit?
A. Between midnight and 6 am
B. At no time
C. When overtaking
D. When the road is clear
438. You must not reverse:
A. Into a side road
B. In a built-up area
C. For longer than necessary
D. For more than a car’s length
439. What does this sign means?

A. Turn left ahead
B. Give way
C. T-junction
D. No through road
440. You are driving on a wet road and you have to stop your vehicle in an emergency. You should:
A. Keep both hands on the wheel
B. Apply the handbrake and footbrake together
C. Select reverse gear
D. Give an arm signal
in an emergency, you will brake hard on the footbrake, which most likely will cause skidding on a wet road. To have a better control of your vehicle, you should keep both of your hands on the steering wheel.
441. You are driving along a narrow country road. When passing the cyclist you should drive
A. Slowly, leaving plenty of room
B. Quickly, leaving plenty of room
C. Quickly, sounding the horn as you pass
D. Slowly, sounding the horn as you pass
Cyclists are more vulnerable in the case. be patient, stay safe, and with courtesy
442. You are driving behind a large vehicle. It signals left but steers to the right. You should:
A. Drive on, keeping to the left
B. Hold your speed and sound your horn
C. Overtake on the right of it
D. Slow down and let the vehicle turn
Large vehicle need more space to make a turn
443. What does this sign mean?

A. Keep in one lane
B. Do not overtake
C. Give way to oncoming traffic
D. Form two lanes
444. It is very windy. You are behind a motorcyclist who is overtaking a high vehicle. What should you do?
A. Keep close to the motorcyclist
B. Stay level with the motorcycle
C. Overtake the motorcyclist immediately
D. Keep well back
445. You see a group of horse riders as you approach a roundabout. They are indicating right but keeping well to the left. You should:

A. Keep close of them
B. Cut in front of them
C. Proceed as normal
D. Stay well back
446. While driving a vehicle, at what distance MUST you be able to read a number plate?
A. 10 meters (33 feet)
B. 30 meters (98 feet)
C. 20.5 meters (67 feet)
D. 15 meters (49 feet)
447. You should never attempt to overtake cyclists
A. When approaching a roundabout
B. On a right hand bend
C. Just before you turn left
D. On narrow road
448. You are approaching a bend at a high speed. You should begin to brake.
A. Before the bend
B. After the bend
C. On the bend
D. After changing gears
449. At an accident a casualty is unconscious but still breathing. You should only move them if
A. There is further danger
B. Bystanders will help you to
C. An ambulance is on its way
D. Bystanders advise you to
450. Your overall stopping distance will be much longer when:
A. Driving on a very hot day
B. Driving in strong winds
C. Driving in fog
D. Driving in rain
451. Why should you make sure your indicators are cancelled after turning?
A. To avoid dazzling other road users
B. To avoid damage to the indicator relay
C. To avoid misleading other road users
D. To avoid flattening the battery
452. Which of these, if allowed to get low, is dangerous?
A. Antifreeze level
B. Battery water level
C. Brake fluid level
D. Radiator coolant level
453. A police officer asks to see your documents. You do not have them with you. You may be asked to take them to the police station with
A. 5 days
B. 7 days
C. 14 days
D. 21 days
454. The age group most likely to be involved in road accidents is
A. 46 to 55-year-olds
B. 30 to 45-year-olds
C. 55 to 66-year olds
D. 17 to 25-year-olds
455. You go to a social event and need to drive a short time after. What precautions should you take?
A. Avoid drinking alcohol on an empty stomach
B. Avoid drinking alcohol completely
C. Drink plenty of coffee after drinking alcohol
D. Drink plenty of milk before drinking alcohol
456. In normal conditions the braking distance when travelling at 50 mph is
A. 25 meters
B. 38 meters
C. 14 meters
D. 16 meters
457. If you notice a strong smell of petrol as you are driving along you should
A. Expect it to stop in a few miles
B. Stop at a suitable place and investigate the problem
C. Not worry, as it is only exhaust fumes
D. Carry on at a reduced speed
458. Which statement represents being in safe control of your vehicle?
A. One hand on the steering wheel and the other simply hanging out of the window to catch the breeze and look cool or wave to friends.
B. One hand on the steering wheel and the other grasping the gear lever for the most part to facilitate instant gear changes.
C. One hand on the steering wheel and the other being used to hold a mobile phone.
D. Both hands on the steering wheel at all times , and only when a change of gear or operation of controls is necessary that one hand is taken off the steering wheel.
459. When emerging from a side road into a queue of traffic which cars can be especially difficult to see?
A. Motorcycles
B. Cars
C. Milk floats
D. Tractors
460. What does this sign mean?
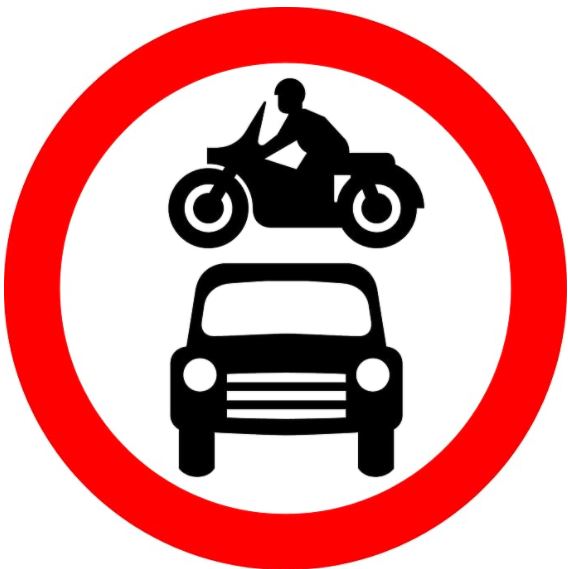

A. No motor vehicles
B. Clearway (no stopping)
C. No overtaking
D. Cars and motorcycles only
461. When going straight ahead at a roundabout you should
A. Indicate left before leaving the roundabout
B. Not indicate at any time
C. Indicate left when approaching the roundabout
D. Indicate right when approaching the roundabout
462. What is most likely to cause high fuel consumption?
A. Poor steering control
B. Staying in high gears
C. Aggressive braking
D. Driving above 50 mph
463. A heavy load on your roof rack will:
A. Make the steering lighter
B. Reduce the stopping distance
C. Reduce stability
D. Improve the road holding
464. You are following a vehicle at a safe distance on a wet and slippery road. Another driver overtakes you and pulls into the gap you have left. What should you do?
A. Stay close to the other vehicle until it moves on
B. Try to overtake safely as soon as you can
C. Drop back to regain a safe distance
D. Flash your headlights as a warning
465. If you are turning left into a side road what hazards should you be especially aware of?
A. Traffic congestion
B. Pedestrians
C. One way street
D. Parked vehicles.
466. At a puffin crossing which light won't you see?
A. Steady amber
B. Red
C. Flashing amber
D. Green
467. To avoid spilling after refueling, you should make sure that:
A. You have used a locking filler cap
B. Your filler cap is securely fastened
C. Your tank is only 3/4 full
D. You check your fuel gauge is working
468. If you are following a car driven by an elderly driver, you should:
A. Stay close behind and drive carefully
B. Expect the driver to drive badly
C. Be aware that the driver’s reactions may not be as fast as yours
D. Flash your lights and overtake
469. In fast moving traffic a two (2) second gap may be enough only when conditions are:
A. Foggy
B. Dry
C. Damp
D. Wet
When road is wet, the stopping distance will be doubled. So on a dry road a 2-second gap will be ok, but on a wet road, you should leave a 4-second gap.
470. Overloading your vehicle can seriously affect?
A. Your comfort
B. Your ability to change gears
C. The steering
D. The Handling
471. You are going straight ahead at a roundabout. How should you signal?
A. Signal right on the approach and then left to leave the roundabout
B. Signal left just after you pass the exit before the one you will take
C. Signal left on the approach to the roundabout and keep the signal on until you leave
D. Signal left as you leave the roundabouts
472. You are dazzled by oncoming headlights when driving at night. What should you do?
A. Slow down or stop
B. Flash your lights
C. Brake hard
D. Drive faster past the oncoming car
473. It is essential that tyre pressures be checked regularly. When should this be done?
A. When tyres are hot
B. After any length journey
C. After travelling at high speed
D. When tyres are cold
474. You are turning right onto a dual carriageway. What should you do before emerging?
A. Position your vehicle well to the left of the side of the road
B. Make sure that you leave enough room for a vehicle behind
C. Stop, apply the handbrake then select a low gear
D. Check that the central reservation is wide enough for your vehicle
475. You enter a road where there are road humps. You should:

A. Accelerate quickly between each one
B. Maintain a reduced speed throughout
C. Drive slowly at school times only
D. Always keep to the maximum legal speed
476. You are following a slow-moving vehicle on a narrow country road. There is a junction just ahead on the right. What should you do?
A. Overtake after checking your mirrors and signaling
B. Stay behind until you are past the junction
C. Slow down and prepare to overtake on the left
D. Accelerate quickly to pass before the junction
477. Who is responsible for ensuring that a vehicle is fully road worthy when driven on a public road?
A. Nobody in particular
B. The VRT tester
C. You, the driver
D. Your mechanic
478. You see a pedestrian with a white stick and red band. This means that the person is
A. Blind only
B. Deaf only
C. Physically disabled
D. Deaf and blind
479. You are following a vehicle on a wet road. You should leave a time gap of at least
A. Four (4) seconds
B. One (1) second
C. Two (2) seconds
D. Three (3) seconds
480. The safest place to park your vehicle at night is
A. On a driveway
B. On a quiet side street
C. In a garage
D. In a car park
481. When the fluid level in your battery is low you should top it up with
A. Water that has been boiled
B. Distilled water
C. Battery acid
D. Tap water
482. What is the meaning of this sign?

A. School crossing patrol
B. National speed limit
C. Waiting restrictions
D. No entry
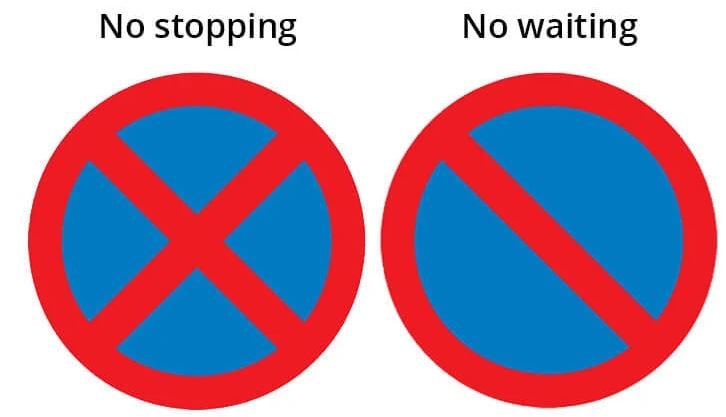

483. You are on a road that has no traffic signs. There are streetlights. What is the speed limit?
A. 30 mph
B. 50 mph
C. 40 mph
D. 20 mph
484. While driving, you intend to turn left into a minor road. On the approach you should:
A. Keep in the middle of the road
B. Keep well to the left of the road
C. Keep just left of the middle of the road
D. Swing out wide just before turning
485. Front fog lights may be used ONLY
A. During ‘lighting up’ times only
B. Between dusk and dawn
C. When visibility is seriously reduced
D. If they are not as bright as the headlights
486. Motorcyclists should wear bright clothing mainly so that
A. The colours are popular
B. It helps keep them cool in summer
C. They must do so by law
D. Other road users can see them more easily
487. What does this traffic sign mean?

A. Give priority to oncoming traffic
B. No overtaking allowed
C. Two way traffic
D. One-way traffic only
Give way to oncoming vehicles.
488. When are passengers allowed to ride in a caravan that is being towed?
A. When travelling on minor roads
B. When they are over 18 years old
C. When travelling on motorways
D. Never
489. When driving in snow it is best to keep in as high a gear as possible. Why is this?
A. So that wheel spin does not cause your engine to run too fast
B. To leave a lower gear available in case of wheel spin
C. To help prevent wheel spin
D. To help you slow down quickly when you brake
490. Travelling on a wet motorway with road spray you should
A. Turn on your hazard lights
B. Turn on your front fog lights
C. Turn on your rear fog lights
D. Turn your headlights to dipped mode
491. Why is coasting wrong or dangerous?
A. There is no engine braking
B. It will cause the car to skid
C. The engine will run faster
D. It will make the engine stall
492. You are to turn right in busy traffic. How would you confirm your intention safely?
A. Flash your headlamp
B. Position over the centre line at an angle
C. Sound the horn
D. Give an arm signal also
493. You are driving on a quiet country road. What should you expect to see coming towards you on YOUR side of the road?
A. Motorcycles
B. Bicycles
C. Pedestrians
D. Horse riders
494. A properly adjusted head rest will:
A. Help you to maintain your driving position
B. Help you to avoid neck injury
C. Make you more comfortable
D. Help you to relax
495. To help prevent your vehicle's radio from being stolen you can
A. Install a cheap, no frills radio
B. Install a security coded radio
C. Park in a busy area
D. Park in a quiet area
496. Excessive or uneven wear in one or more tyres can be caused by faults in the:
A. Braking system
B. Gearbox
C. Steering Wheel
D. Exhaust system
Braking system and suspension may cause excessive or uneven wear of the tyres
497. A driver pulls out of a side road in front of you. You have to brake hard. You should
A. Overtake as soon as possible
B. Ignore the error and stay calm
C. Sound your horn to show your annoyance
D. Flash your lights to show your annoyance
498. Using front/rear fog lights in good visibility will:
A. Dazzle other drivers
B. Flatten the battery
C. Improve your visibility
D. Increase your awareness
499. You are travelling along the left-hand lane of a three-lane motorway. Traffic is joining from a slip road. You should
A. Race the other vehicles
B. Switch on your hazard lights
C. Move to another lane
D. Maintain a steady speed
500. The right hand lane on a three-lane motorway is used for
A. Cruising at low speeds
B. Cruising at high speeds
C. High-sided vehicles
D. Overtaking
501. You are driving behind a large vehicle. It signals left but steers to the right. You should:
A. Slow down and let the vehicle turn
B. Overtake on the right of it
C. Hold your speed and sound your horn
D. Drive on, keeping to the left
502. Car passengers MUST wear a seat belt if one is available, unless they are
A. Travelling within a congestion charging zone
B. In a vehicle fitted with airbags
C. Sitting in the rear seat
D. Exempt for medical reasons
503. It is very blustery and windy. You are about to overtake a motorcyclist. You should:
A. Overtake slowly
B. Keep close as you pass
C. Sound your horn
D. Allow extra room
504. You wish to overtake a long, slow moving vehicle or lorry on a busy road with oncoming traffic. You should:
A. Keep well back until you can see that it is clear
B. Stay behind until the driver waves you past
C. Follow it closely and keep moving out to see the road ahead
D. Flash your headlights for the oncoming traffic to give way
505. What does a sign with a brown background show?

A. Tourist directions
B. Primary roads
C. Minor routes
D. Motorway routes
506. When should you especially check the engine oil level?
A. On a cold morning
B. Before starting a long journey
C. Before an MOT test
D. Every 5000 miles
507. You are driving on a dual-carriageway with surface spray. You should:
A. Your dipped headlights
B. Your hazard flashers
C. Your sidelights
D. Your rear fog lights
508. You are approaching a busy junction. There are several lanes with road markings. At the last moment you realise that you are in the wrong lane. You should:
A. Use clear arm signals to cut across
B. Force your way across
C. Continue in that lane
D. Stop until the area has cleared
509. A learner driver you are following stalls at a junction. What should you do?
A. Shout instructions
B. Be patient and wait for them to move on
C. Steer around them and drive on
D. Sound your horn and flash your lights
510. An elderly person’s driving ability could be affected because they may be unable to:
A. React very quickly
B. Understand road signs
C. Give signals correctly
D. Obtain car insurance
511. What action should you take when elderly people are crossing the road?
A. Wave them across so they know that you have seen them
B. Rev the engine to let them know that you are waiting
C. Tap the horn in case they are hard of hearing
D. Be patient and allow them to cross in their own time
512. Triangular road signs give:
A. Warnings
B. Instructions
C. Information
D. Directions
513. You see this traffic light ahead. Which light(s) will come on next?

A. Red and amber together
B. Green alone
C. Red alone
D. Green and amber together
514. How should you correct a rear wheel skid?
A. Steer away from it
B. Remove your hand's from the steering wheel and let the vehicle steer itself
C. Brake hard and not steer at all
D. Steer into it
515. You are looking for somewhere to park your vehicle. The area is full EXCEPT for spaces marked ‘disabled use’. You can:
A. Not park there unless permitted
B. Use these spaces, disabled or not
C. Park if you stay with your vehicle
D. Use these spaces when elsewhere is full
516. You are taking drugs that are likely to affect you driving. What should you do?
A. Only drive if accompanied by a full licence holder
B. Limit your driving to essential journeys
C. Seek medical advice before driving
D. Drive only for short distances
516. You are taking drugs that are likely to affect you driving. What should you do?
A. Drive only for short distances
B. Only drive if accompanied by a full licence holder
C. Limit your driving to essential journeys
D. Seek medical advice before driving
517. Motorcyclists often look round over their right shoulder just before turning right. This is because
A. They need to check for traffic in their blind area
B. Motorcycles do not have mirrors
C. They need to listen for following traffic
D. Looking around helps them balance as they turn
518. To help keep your vehicle secure at night where should you park?
A. On a red route
B. In a well-lit area
C. In a quiet road
D. Near a police station
519. Where may you overtake on a one-way Street?
A. Only on the right-hand side
B. Overtaking is not allowed
C. Only on the left-hand side
D. Either on the right or the left
520. Why should you particularly look for motorcyclists and cyclists at any junction?
A. They are harder to see
B. They may slow down to let you turn
C. They might not see you turn
D. They nay want to turn into the side road
521. You want to turn right from a main road into a side road. Just before you turn you should
A. Stop and set the handbrake
B. Cancel your right-turn signal
C. Check for traffic overtaking on your right
D. Select first gear
522. Your doctor has given you a course of medicine. Why should you ask if it is OK to drive?
A. You will have to let your insurance company know about the medicine
B. Some types of medicine can cause your reactions to slow down
C. The medicine you take may affect your hearing
D. Drugs make you a better driver by quickening your reactions
523. You arrive at an accident where someone is suffering from severe burns. You should:
A. Burst any blisters
B. Remove anything stuck to the burns
C. Apply lotions to the injury
D. Douse the burns with cool liquid
524. You are approaching a bend at a high speed. You should begin to brake.
A. Before the bend
B. After changing gears
C. On the bend
D. After the bend
525. In some residential roads you will find a speed limit of:
A. 40 mph
B. 60 mph
C. 50 mph
D. 25 mph
526. You are driving on a multi-lane carriageway. By mistake, you go past the exit that you wanted to take. You should:
A. Carefully reverse on the hard shoulder
B. Carefully reverse in the left-hand lane
C. Make a U-turn at the next gap in the central reservation
D. Carry on to the next exit
527. You are driving and ahead of you there is a vehicle with a flashing amber beacon. This means it is:
A. Slow moving
B. A school crossing patrol
C. Broken down
D. A doctor’s car
528. Why should you make sure that you have cancelled your indicators after turning?
A. To avoid flattening the battery
B. To avoid dazzling other road users
C. To avoid damage to the indicator relay
D. To avoid misleading other road users
529. 'Tailgating' usually means
A. Reversing into a parking space
B. Following another vehicle too closely
C. Using the rear door of a hatchback car
D. Driving with rear fog lights on
Tailgating, or following too closely behind another vehicle is a dangerous practice.
530. Where are you most likely to be affected by a side wind?
A. On a narrow country lane
B. On a long, straight road
C. On an open stretch of road
D. On a busy stretch of road
531. A horse rider is in the left-hand lane approaching a roundabout. The driver behind should expect the rider to:
A. Go ahead
B. Turn left
C. Go in any direction
D. Turn right
532. There is vibration on your steering wheel as you drive at certain speeds. You should check that the:
A. Wheels are balanced
B. Doors are closed
C. Exhaust is not loose
D. Engine oil level is correct
Unbalance wheels will cause vibration of steering wheel
533. You are parking on a two-way road at night. The speed limit is 40 mph. You should park on the
A. Left with parking lights on
B. Right with parking lights on
C. Right with dipped headlights on
D. Left with no lights on
534. You arrive at the scene of a motorcycle accident and the rider is injured. When should the helmet be removed?
A. Always, unless they are in shock
B. Only when the motorcyclist asks
C. Only when it is essential
D. Always straight away
It is important not to remove their helmet unless it is necessary to do so to keep them alive.
535. You stopped for pedestrians waiting to cross at a zebra crossing. They did not start to cross. What should you do?
A. Be patient and wait
B. Drive on
C. Sound your horn
D. Wave them to cross
Always be patient and considerate at zebra cross, not only because pedestrians have the right of way.
536. 'Red Routes' in major cities have been introduced to
A. Provide better parking
B. Help the traffic flow
C. Raise the speed limits
D. Allow lorries to load more freely
537. You are trying to move off on snow. You should use
A. A high engine speed
B. The lowest gear you can
C. The handbrake and footbrake together
D. The highest gear you can
538. When you approach a bus that is about to move off from a bus stop you should:

A. Get past before it moves
B. Signal left and wave the bus on
C. Allow it to pull away, if it is safe to do so
D. Flash your headlights as you approach
539. There is a tractor ahead of you. You wish to overtake but you are NOT sure if it is safe to do so. You should:
A. Follow another overtaking vehicle through
B. Speed through but flash your lights to oncoming traffic
C. Not overtake if you are in doubt
D. Sound your horn to the slow vehicle to pull over
540. You are turning left on a slippery road. The back of your vehicle slides to the right. You should:
A. Brake firmly and not turn the steering wheel
B. Brake firmly and steer to the left
C. Steer carefully to the right
D. Steer carefully to the left
Continue to turn left will cause the car to spin.
541. Motorcars must first have an MOT certificate when they are
A. Five (5) years old
B. One (1) year old
C. Three (3) years old
D. Seven (7) years old
542. For a driver, what doe the term Blind Spot mean?
A. An area not seen in your mirrors
B. The area covered by your left mirror
C. An area immediately behind the car
D. The area covered by the rear view mirror
543. It is illegal to drive with tyres that -
A. Were bought second-hand
B. Are more than three years old
C. Are of different makes
D. Have a large, deep cut in the sidewall
544. What does the sign mean?
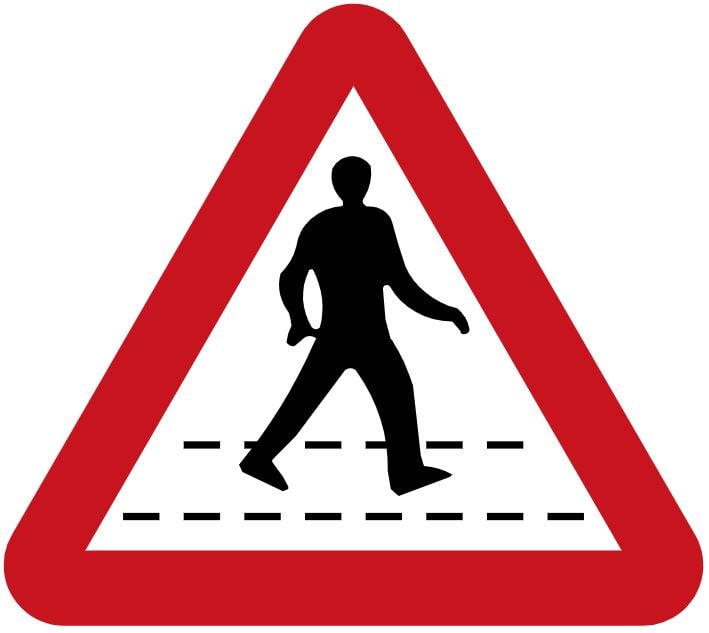

A. Pedestrian crossing ahead
B. School crossing patrol
C. Pedestrian zone – no vehicles
D. No pedestrians allowed
545. You are towing a caravan. Which is the safest type of rear-view mirror to use?
A. Interior wide-angle mirror
B. Extended-arm side mirrors
C. Ordinary interior mirror
D. Ordinary door mirrors
546. At an incident it is important to look after any casualties. When the area is safe you should
A. Give them a drink
B. Get them out of the vehicle
C. Give them something to eat
D. Keep them in the vehicle
547. You engine catches fire what should you do first?
A. Lift the bonnet and disconnect the battery
B. Call a breakdown service
C. Call the fire brigade
D. Lift the bonnet and warn other traffic
548. Unbalanced wheels on a car may cause
A. Poor braking
B. The tyres to wear out
C. Poor acceleration
D. The steering to vibrate
549. You are at the front of a queue of traffic waiting to turn right into a side road. Why is it important to check your right mirror just before turning?
A. To look for pedestrians about to cross
B. To make sure the side road is clear
C. To check for emerging traffic
D. To check for overtaking vehicles
550. Before you make a U-turn in the road, you should
A. Signal so that other drivers can slow down for you
B. Give an arm signal as well as using your indicators
C. Look over your shoulder for a final check
D. Select a higher gear than normal
551. What does this sign mean?
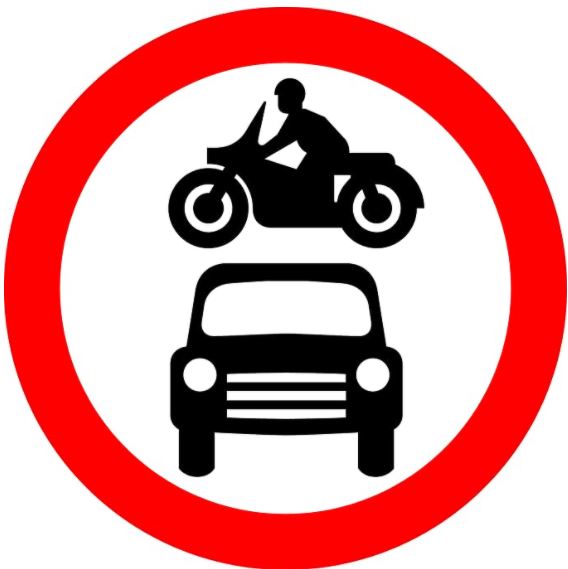

A. Cars and motorcycles only
B. No motor vehicles
C. Clearway (no stopping)
D. No overtaking
552. A driver can only read a number plate at the required distance with glasses on. The glasses should be worn:
A. Only when reversing
B. Only when driving long distances
C. Only in poor visibility
D. All the time when driving
553. You are following a vehicle on a wet road. You should leave a time gap of at least
A. Two (2) seconds
B. One (1) second
C. Four (4) seconds
D. Three (3) seconds
554. A newly qualified driver must
A. Be accompanied on a motorway
B. Have valid motor insurance
C. Display green L-Plates
D. Not exceed 40 mph for 12 months
555. You have too much oil in your engine. What could this cause?
A. Chain wear
B. Engine overheating
C. Low oil pressure
D. Oil leaks
556. You should avoid 'coasting' your car because it could:
A. Increase tyre wear
B. Damage the suspension
C. Flatten the battery
D. Reduce steering control
557. What is the meaning of this sign?

A. Traffic queues likely
B. Light signals ahead at a level crossing
C. Accident black spot ahead
D. Pedestrian crossing ahead
558. When going straight ahead at a roundabout you should:
A. Not indicate at any time
B. Indicate left when approaching the roundabout
C. Indicate right when approaching the roundabout
D. Indicate left before leaving the roundabout
559. At which pedestrian crossing are cyclists allowed to ride across?
A. Zebra
B. Toucan
C. Puffin
D. Pelican
560. You are waiting in a traffic queue at night. To avoid dazzling the drivers behind, you should:
A. Apply the footbrake only
B. Use both the handbrake and footbrake
C. Switch off your headlights
D. Apply the handbrake only
N.B. the brake light will be switched on when using the footbrake
561. When driving through a Ford or flood water, what gear should you use?
A. Reverse
B. Fifth
C. First or second
D. Fourth
E. Third
562. You are driving behind three cyclists. They approach a roundabout in the left hand lane. In which direction should you expect the cyclists to go?
A. Any direction
B. Left
C. Right
D. Straight ahead
563. What is the national speed limit on motorways, unless otherwise indicated, for cars and motorcycles?
A. 60mph
B. 70mph
C. 50mph
D. 80mph
564. An elderly person's driving ability could be affected because they may be unable to
A. Give signals correctly
B. Obtain car insurance
C. React very quickly
D. Understand road signs
565. Where should you take particular care to look out for motorcyclists and cyclists?
A. On dual carriageways
B. At junctions
C. At zebra crossings
D. On one-way streets
566. When following a vehicle on a wet road you should leave a time gap of at least:
A. 1 second
B. 4 seconds
C. 2 seconds
D. 5 seconds
567. This marking appears on the road just before a
A. Stop sign
B. No through road sign
C. No entry sign
D. Give way sign
568. What MUST you do when you see this sign?

A. Stop, ONLY if children are waiting to cross
B. Stop, even if the road is clear
C. Stop, ONLY if traffic is approaching
D. Stop, ONLY if a red light is showing
569. You are following a slow-moving vehicle on a narrow country road. There is a junction just ahead on the right. What should you do?
A. Overtake after checking your mirrors and signaling
B. Stay behind until you are past the junction
C. Slow down and prepare to overtake on the left
D. Accelerate quickly to pass before the junction
570. As a driver what do you understand by the term 'Blind Spot'?
A. An area not covered by your headlights
B. An area covered by your right hand mirror
C. An area covered by your left hand mirror
D. An area not seen in your mirrors
Blind spots are the areas of the road that cannot be seen while looking forward or through either the rear-view or side mirrors
571. You are on a narrow road at night. A slower-moving vehicle ahead has been signaling right for some time. What should you do?
A. Wait for the signal to be cancelled before overtaking
B. Signal right and sound your horn
C. Flash your headlights before overtaking
D. Overtake on the left
572. You may only enter a box junction when:

A. The traffic lights show green
B. You need to turn left
C. There are less than two vehicles in front of you
D. Your exit road is clear
573. You turn into a side road. Pedestrians have started to cross the road. You should
A. Give way to them
B. Drive around them
C. Proceed regardless
D. Flash your lights and wave them across
574. What does tailgating mean?
A. Driving with your headlights on full beam
B. Bumping another car whilst parking
C. Following another vehicle too closely
D. Skidding on a dry road
575. When are passengers allowed to ride in a caravan that is being towed?
A. Never
B. When travelling on motorways
C. When they are over 18 years old
D. When travelling on minor roads
576. You are about to go down a steep hill. To control the speed of your car you should:
A. Select a high gear and use the brakes firmly
B. Select a low gear and avoid using the brakes
C. Select a low gear and use the brakes carefully
D. Select a high gear and use the brakes carefully
577. Super trams or Light Rapid Transit (LRT) systems are environmentally friendly because
A. They use electric power
B. They use quieter roads
C. They use diesel power
D. They do not operate during rush hour
578. You are driving behind a moped or small motorcycle. You want to turn left just ahead. You should:
A. Stay behind until the moped has passed the junction
B. Pull alongside the moped and stay level until just before the junction
C. Sound your horn as a warning and pull in front of the moped
D. Overtake the moped before the junction
579. Which of the following is the main cause of rear-end collisions?
A. Pedestrians crossing the road unexpectedly
B. Driving too close to the vehicle in front
C. A wet road surface
D. Traffic lights
580. When you are overtaking a horse and rider you should:
A. Flash your headlights as a warning
B. Go past as quickly as possible
C. Go past slowly and carefully
D. Sound your horn as a warning
581. A red traffic light means:
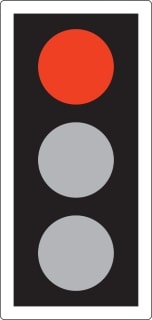
A. You must slow down and prepare to stop if traffic has started to cross
B. You must stop behind the white stop line
C. You may drive straight on if there is no other traffic
D. You may turn left if it is safe to do so
582. You are driving a slow moving car on a narrow winding road. In order to let other vehicles overtake you should
A. Show a left turn signal
B. Keep left and hold your speed
C. Pull in safely when you can
D. Wave to them to pass
Safety is the first priority
583. You are about to drive home. You cannot find the glasses you need to wear when driving. You should:
A. Drive home slowly, keeping to quite roads
B. Borrow a friend’s glasses and drive home
C. Find a way of getting home without driving
D. Drive home at night
584. When turning your car in the road, you must:
A. Keep your hand on the handbrake
B. Overhang the kerb
C. Use an available driveway
D. Check all around for other road users
Look out for other road users when turning, especially pedestrians
585. Road humps, chicanes, and road narrowing's are
A. Always at major road works
B. Used to increase traffic speed
C. At toll-bridge approaches only
D. Traffic calming measures
586. When travelling on ice braking distances can be
A. Three (3) times the normal distance
B. Ten (10) times the normal distance
C. Six (6) times the normal distance
D. fifteen (15) times the normal distance
587. You stop for pedestrians waiting to cross at a zebra crossing. They do not start to cross. What should you do?
A. Wave then to cross
B. Be patient and wait
C. Carry on
D. Sound your horn
588. A strong cross wind is least likely to affect which of these vehicles?
A. Cyclists
B. Motorcycles
C. Cars
D. High-sided vehicles
589. While driving a vehicle, at what distance MUST you be able to read a number plate?
A. 30 meters (98 feet)
B. 20.5 meters (67 feet)
C. 15 meters (49 feet)
D. 10 meters (33 feet)
590. What is the most common cause of road accidents?
A. Driver error
B. Mechanical failure
C. Road conditions
D. Weather conditions
591. As you approach a pelican crossing the lights change to green but elderly people are halfway across. You should:
A. Flash your lights in case they have not heard you
B. Wave them to cross as quickly as they can
C. Rev your engine to make them hurry
D. Wait because they will take longer to cross
592. You are following a learner driver who stalls at a junction. You should
A. Start to rev your engine if they take too long to restart
B. Immediately steer around them and drive on
C. Stay very close behind and flash your headlights
D. Be patient as you expect them to make mistakes
593. Which vehicle may have to use a different course to normal at roundabouts?
A. Van
B. Long vehicle
C. Estate car
D. Sports car
594. You are overtaking a car at night. You must be sure that:
A. You flash your headlamps before overtaking
B. You do not dazzle other road users
C. You have switched your lights to full beam before overtaking
D. Your rear fog lights are switched on
595. When may you sound the horn on your vehicle?
A. To warn others of your presence
B. To make slower drivers move over
C. To attract a friend’s attention
D. To give you right of way
596. On a motorway what is used to reduce traffic bunching?
A. Variable speed limits
B. National speed limits
C. Contraflow systems
D. Lane closures
597. You are driving in busy traffic. You want to pull up on the left just after a junction on the left. When should you signal?
A. It would be better not to signal at all
B. As you are passing or just after the junction
C. Just before you reach the junction
D. Well before you reach the junction
598. Whilst driving you have an accident in which someone is injured. You must report this to the police within
A. 7 days
B. 24 hours
C. 36 hours
D. 12 hours
599. You are carrying a child in your car. They are under three years of age. Which of these is a suitable restraint?
A. An adult seat belt
B. A child seat
C. An adult lap belt
D. An adult holding a child
600. What is the maximum speed limit in a built up area unless indicated otherwise?
A. 60mph
B. 30mph
C. 50mph
D. 40mph
601. You are travelling in heavy rain. Your overall stopping distance is likely to be
A. Quadrupled
B. Up to 15 times greater
C. Doubled
D. Tripled
602. You are driving on a dual carriageway. You have to slow down quickly due to a hazard. You should:
A. Sound your horn
B. Switch on your hazard lights
C. Switch on your headlights
D. Flash your headlights
603. Your car hits a pedestrian at 60 kph. The pedestrian will:
A. Certainly survive
B. Probably be killed
C. Probably survive
D. Certainly be killed
Speed kills - The relationship between speed and injury severity is particularly critical for vulnerable road users such as pedestrians and cyclists. For example, pedestrians have been shown to have a 90% chance of survival when struck by a car travelling at 30 km/h (18 mph) or below, but less than 50% chance of surviving an impact at 45 km/h (28 mph). Pedestrians have almost no chance of surviving an impact at 80 km/hr (50 mph).
604. When must you stop at this junction?
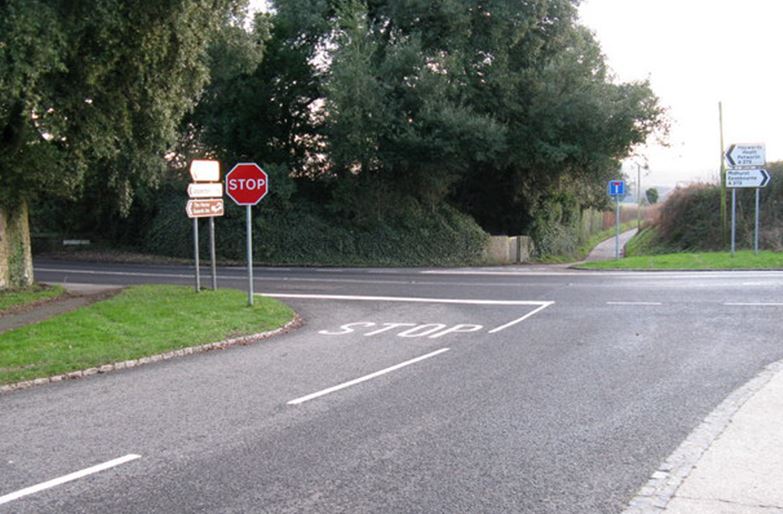

A. Only when the area is busy
B. At all times
C. When turning right only
D. During rush hours only
605. Who is especially in danger of not being seen as you reverse your car?
A. Cyclists
B. Children
C. Motorcyclists
D. Car drivers
606. A driver pulls out of a side road in front of you. You have to brake hard. You should
A. Ignore the error and stay calm
B. Flash your lights to show your annoyance
C. Sound your horn to show your annoyance
D. Overtake as soon as possible
607. You think the driver in the vehicle in front has forgotten to cancel their right indicator. You should
A. Flash your lights to alert the driver
B. Stay behind and not overtake
C. Overtake on the left if there is room
D. Sound your horn before overtaking
608. Vehicles fitted with an anti-lock brake system
A. Can be steered while you are braking
B. Are impossible to skid
C. Are not fitted with a handbrake
D. Accelerate much faster
609. You are approaching this roundabout and see the cyclist signal right. Why is the cyclist keeping to the left?

A. The cyclist is going to turn left instead
B. The cyclist thinks The highway Code does not apply to bicycles
C. It is quicker route for cyclist
D. The cyclist is slower and more vulnerable
610. At an accident a small child is not breathing. When giving a mouth to mouth you should breathe
A. Heavily
B. Rapidly
C. Gently
D. Sharply
611. When you are overtaking a cyclist in the road, you should leave as much room as you would give to a car. What is the main reason for this?
A. The cyclist might have to make a right turn
B. The cyclist might swerve
C. The cyclist might get off the bike
D. The cyclist might change lanes
612. You are signaling to turn right in busy traffic. How would you confirm your intention safely?
A. Give an arm signal
B. Position over the centre line
C. Flash your headlights
D. Sound the horn
613. When may you use hazard warning lights?
A. When you are being towed
B. To park on double yellow lines
C. When you have broken down
D. To park alongside another car
614. You are driving on a narrow country road. Where would you find it most difficult to see horses and riders ahead of you?
A. On right-hand bends
B. On left-hand bends
C. When uphill
D. When downhill
615. A police officer asks to see your documents. You do not have them with you. You may be asked to take them to the police station with
A. 14 days
B. 5 days
C. 7 days
D. 21 days
616. Front fog lights may be used ONLY if:
A. They are not as bright as the headlights
B. Visibility is seriously reduced
C. An audible warning device is used
D. They are fitted above the bumper
617. You are on a dual carriageway. Ahead you see a vehicle with an amber flashing light. What could this be?
A. A disabled person`s vehicle
B. A doctor on call
C. A fire engine
D. An ambulance
618. The driver of this car is giving an arm signal. What is he about to do?

A. Go straight ahead
B. Let pedestrians cross
C. Turn to the right
D. Turn to the left
619. What should you do if a driver pulls out of a side road in front of you and you have to brake hard?
A. Overtake as soon as possible
B. Flash your lights to show your annoyance
C. Sound your horn to show your annoyance
D. Ignore the error and stay calm
Try to be tolerant if a vehicle does emerge and you have to brake quickly and don't react aggressively.
620. Catalytic converters are fitted to make the
A. Exhaust systems easier to replace
B. Engines run quietly
C. Engines produce more power
D. Exhaust fumes cleaner
621. Before overtaking a large vehicle or lorry you should keep well back. Why is this?
A. To leave a gap in case stops and rolls back
B. To get the best view of the road ahead
C. To offer other drivers a safe gap if they want to overtake you
D. To give acceleration space to overtake quickly on blind bends
622. A roof rack that is fitted to your car will:
A. Make your car go faster
B. Improve the road handling
C. Reduce fuel consumption
D. Increase fuel consumption
623. When driving in falling snow you should
A. Brake firmly and quickly
B. Use sidelights only
C. Be ready to steer sharply
D. Brake gently in plenty of time
624. What is the meaning of this sign?

A. Uneven road surface
B. Humpback bridge
C. Humps on the road
D. Risk of grounding
The Risk of Grounding sign informs drivers they are approaching a level crossing railway line or a hump backed bridge ahead where there may be a risk of grounding.
625. When you are NOT sure it is safe to reverse your vehicle you should
A. Rev your engine
B. Use your horn
C. Get out and check
D. Reverse slowly
626. You are to turn right in busy traffic. How would you confirm your intention safely?
A. Position over the centre line at an angle
B. Flash your headlamp
C. Sound the horn
D. Give an arm signal also
627. You are approaching two cyclists. They approach a roundabout in the left-hand lane. In which direction should you expect the cyclists to go?
A. Any direction
B. Right
C. Straight ahead
D. Left
628. Your overall stopping distance will be much longer when:
A. Driving in fog
B. Driving on a very hot day
C. Driving in rain
D. Driving in strong winds
629. Front fog lights may be used ONLY
A. When visibility is seriously reduced
B. Between dusk and dawn
C. During ‘lighting up’ times only
D. If they are not as bright as the headlights
630. If a friend wants to teach you to drive a car, they must:
A. Be over 18 and hold an advanced driver’s certificate
B. Be over 21 and have had a full license for at least three years.
C. Be over 18 and have fully comprehensive insurance
D. Be over 23 and have held a full licence for at least 5 years
631. You are driving in the left-hand lane of a dual carriageway. Another car overtakes and pulls in front of you leaving you without enough separation distance. You should:
A. Continue as you are
B. Sound your horn
C. Drop back
D. Move to the right-hand lane
632. You are approaching a crossroads. The traffic lights have failed. What should you do?
A. Be prepared to brake sharply to a stop
B. Be prepared to stop for any traffic
C. Brake sharply to a stop before looking
D. Brake and stop only for large vehicles
633. Some two-way roads are divided into three lanes. Why are these particularly dangerous?
A. Traffic can travel faster in poor weather conditions
B. Traffic in both directions can use the middle lane to overtake
C. Traffic can overtake on the left
D. Traffic uses the middle lane for emergencies only
634. A provisional licence holder must not drive a motorcar
A. On a dual carriageway
B. Alone
C. With passengers in the back
D. At night
635. What should you do when overtaking a motorcyclist in strong winds?
A. Pass immediately
B. Pass quickly
C. Pass wide
D. Pass close
636. A strong crosswind is least likely to affect which of these vehicles?
A. Motorcycles
B. Cars
C. Cyclists
D. High-sided vehicles
637. When driving at 60mph on a dry road what would be the shortest overall stopping distance?
A. 53 meters
B. 73 meters
C. 96 meters
D. 58 meters
638. When may you reverse from a side-road into a main road?
A. Only if both roads are clear of traffic
B. Not at any time
C. At any time
D. Only if the main road is clear of traffic
639. You are driving down a long steep hill. You suddenly notice that your brakes are not working as well as normal. What is the usual cause of this?
A. Oil on the brakes
B. Badly adjusted
C. The brakes overheating
D. Air in the brake fluid
640. If a trailer swerves or snakes when you are towing it you should
A. Ease off the accelerator and reduce your speed
B. Brake hard and hold the pedal down
C. Increase your speed as quickly as possible
D. Let go of the steering wheel and let it correct itself
641. You are driving a slow moving car on a narrow road. When traffic wishes to overtake you should
A. Pull in safely as soon as you can do so
B. Stop immediately and wave it on
C. Put your hazard warning lights on
D. Take no action
Safety is 1st priority, and at the same time try to keep a smooth traffic flow
642. You are at a junction controlled by traffic lights. When should you NOT proceed at green?

A. When pedestrians are waiting to cross
B. When you think the lights may be about to change
C. When you intend to turn right
D. When your exit from the junction is blocked
643. It is very windy. You are behind a motorcyclist who is overtaking a high-sided vehicle. What should you do?
A. Keep close to the motorcyclist
B. Stay level with the motorcyclist
C. Keep well back
D. Overtake the motorcyclist immediately
644. When following a vehicle on a wet road you should leave a time gap of at least?
A. 4 seconds
B. 3 seconds
C. 2 seconds
D. 1 second
645. When approaching a right-hand bend you should keep well to the left. Why this?
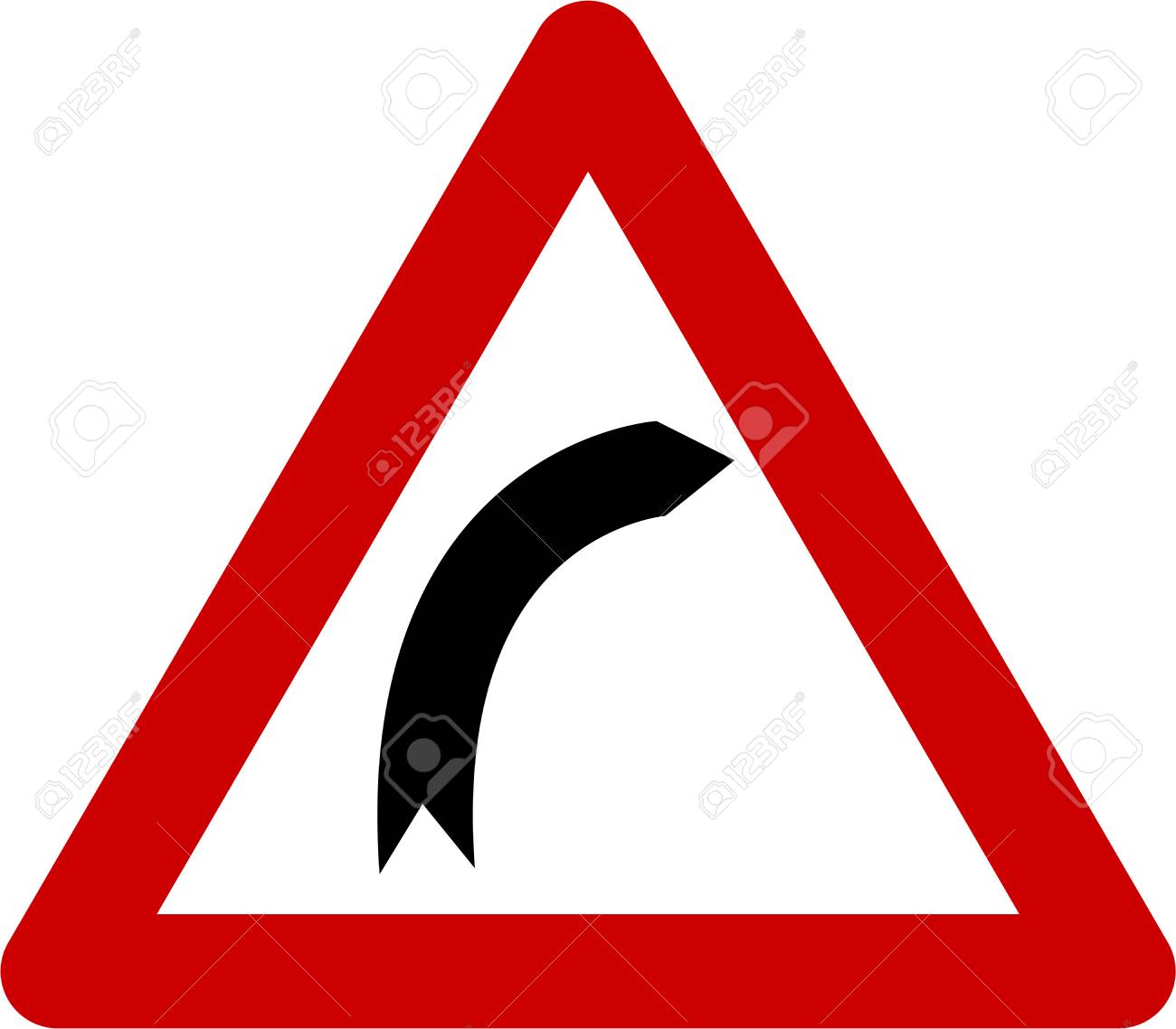

A. To improve your view of the road
B. To let faster traffic from behind overtake
C. To overcome the effect of the road’s slope
D. To be positioned safely if the vehicle skids
646. Which of these, if allowed to get low, is dangerous?
A. Antifreeze level
B. Battery water level
C. Radiator coolant level
D. Brake fluid level
It will be extremely dangerous if you could not slow down and stop your vehicle
647. You are driving at the legal speed limit. A vehicle behind tries to overtake. Should you try to prevent the driver overtaking?
A. No, unless it is safe to do so
B. Yes, because the other driver is acting dangerously
C. No, not at any time
D. Yes, because the other driver is breaking the law
Try to give way to other road users when it is safe to do so
The Official DVSA Theory Test Kit for Car Drivers - DVD-ROM
The Official DVSA Theory Test Kit for Car Drivers - PAPERBACK
Theory Test - Mock Papers - DVSA Revision Questions
There are 1000+ questions in the DVSA theory test question bank, study these comprehensive revision guides and you will pass the the UK driving theory test first time.
www.drivinginstructorwebsites.co.uk is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to amazon.com. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases. www.drivinginstructorwebsites.co.uk participates in various other affiliate programs, and we sometimes get commission through purchases made through our links.


